Defining Manufacturing Traveler
A manufacturing traveler is a document, either physical or digital, used to track and manage the flow of materials, components, or instructions throughout a manufacturing process. It serves as a vital communication tool, ensuring consistent execution and efficient workflow. This paper-based or electronic record details the specific steps, procedures, and required resources for each stage of production.
Manufacturing travelers, whether paper or electronic, are fundamental to coordinating operations across different departments and ensuring the timely completion of tasks. They enable manufacturers to optimize their production processes, streamline workflows, and minimize errors. They are especially useful in industries with complex production lines and intricate processes.
Types of Manufacturing Travelers
Manufacturing travelers come in various forms, each tailored to specific needs and industries. Paper travelers are traditional methods of tracking, often used in smaller businesses or for simple processes. Electronic travelers, on the other hand, offer greater flexibility and efficiency in larger, more complex operations.
Uses of Manufacturing Travelers Across Industries
Manufacturing travelers find applications across diverse industries. In automotive manufacturing, they track the movement of parts from assembly to final testing. In electronics production, they ensure components are correctly assembled and tested at each stage. In food processing, travelers might track ingredients and ensure quality standards are met. In short, any industry requiring a detailed, step-by-step production process can benefit from using manufacturing travelers.
Evolution of Manufacturing Travelers
The evolution of manufacturing travelers mirrors the advancement of technology. Early forms, often hand-written on paper, were simple and limited in scope. As technology progressed, electronic travelers emerged, offering greater accuracy, traceability, and data management capabilities. This shift has enabled manufacturers to optimize processes and make real-time adjustments based on data collected from travelers. Today, advanced traveler systems can be integrated with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software, further streamlining operations and improving overall efficiency.
Key Features and Benefits of Different Traveler Types
| Type | Features | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paper | Simple design, readily available, low initial investment. | Easy to understand, tangible record, accessible offline. | Prone to errors, difficult to manage large volumes, limited data analysis capabilities, and lack of real-time updates. |
| Electronic | Digital format, easily modifiable, data-driven insights, real-time tracking, integration with other systems. | Reduced errors, improved efficiency, streamlined workflows, enhanced data analysis, and better traceability. | Requires computer access, potentially higher initial investment for software and training, and reliance on technology and potential for system failure. |
Function and Purpose: Manufacturing Traveler

Manufacturing travelers are essential tools in modern production environments. They act as a centralized, paper-based or digital, system for tracking and managing the flow of materials, parts, and products throughout the various stages of manufacturing. This detailed record-keeping ensures that production runs smoothly, materials are accounted for, and schedules are met. Travelers play a crucial role in connecting different departments and teams within a manufacturing facility, fostering communication and coordination.
Manufacturing travelers provide a vital link between planning and execution, ensuring materials and products move through the production process efficiently and in accordance with the predetermined schedule. This systematic approach allows manufacturers to maintain visibility and control over the entire production pipeline, ultimately improving efficiency and reducing errors.
Primary Function of a Manufacturing Traveler
The primary function of a manufacturing traveler is to document the journey of a specific product or material through the production process. This detailed documentation encompasses every step, from raw material arrival to finished goods shipment. The traveler serves as a single source of truth, providing a complete history of the item’s progress.
How Manufacturing Travelers Support the Production Process
Travelers support the production process by providing a clear, step-by-step guide for the movement and processing of materials. This transparency allows for efficient resource allocation and reduces delays. By meticulously tracking the progress of each item, manufacturers can identify bottlenecks and optimize the production flow. Travelers also assist in maintaining accurate records of inventory, ensuring that materials are used effectively and preventing waste.
Role of Travelers in Tracking Materials, Parts, and Products
Manufacturing travelers are vital for tracking materials, parts, and products throughout the entire production cycle. Each traveler typically includes a unique identifier, allowing for precise tracking and traceability. This information is crucial for quality control, inventory management, and resolving issues quickly if they arise. This meticulous tracking also aids in identifying potential inefficiencies in the production process.
Comparison of Traveler Use in Different Manufacturing Stages
The specific use of manufacturing travelers varies depending on the stage of production. In the raw material receiving stage, travelers are used to document the arrival and inspection of incoming materials. During production line operations, travelers track the movement of parts through each stage of processing, noting any quality checks or adjustments made. In the final stages, travelers are used to track the product’s journey to packaging and shipment.
Traveler Use in Maintaining Production Schedules
Travelers play a significant role in maintaining production schedules. They track the time spent on each operation and identify any delays or discrepancies. This information helps in adjusting schedules, re-allocating resources, and preventing production bottlenecks. The detailed data collected on travelers allows for better predictive analysis of future production runs.
Table Illustrating Traveler Usage Across Manufacturing Stages
| Manufacturing Stage | Traveler Role | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Receiving | Document receipt, inspection, and initial allocation of raw materials. | Recording the quantity and quality of received steel, logging any discrepancies, and assigning the material to the appropriate production order. |
| Production Line | Track part movement through each workstation, record processing times, and indicate any quality control checks. | Tracking a circuit board through the soldering, testing, and assembly stations, noting the completion time at each step and any rework required. |
| Quality Control | Document quality checks and approvals. | Recording the results of visual inspections, functional tests, and other quality assessments. |
| Packaging and Shipping | Verify completed products, record packaging details, and track shipment information. | Confirming the quantity and condition of finished goods, noting packaging materials used, and generating shipping labels. |
Modern Applications and Trends
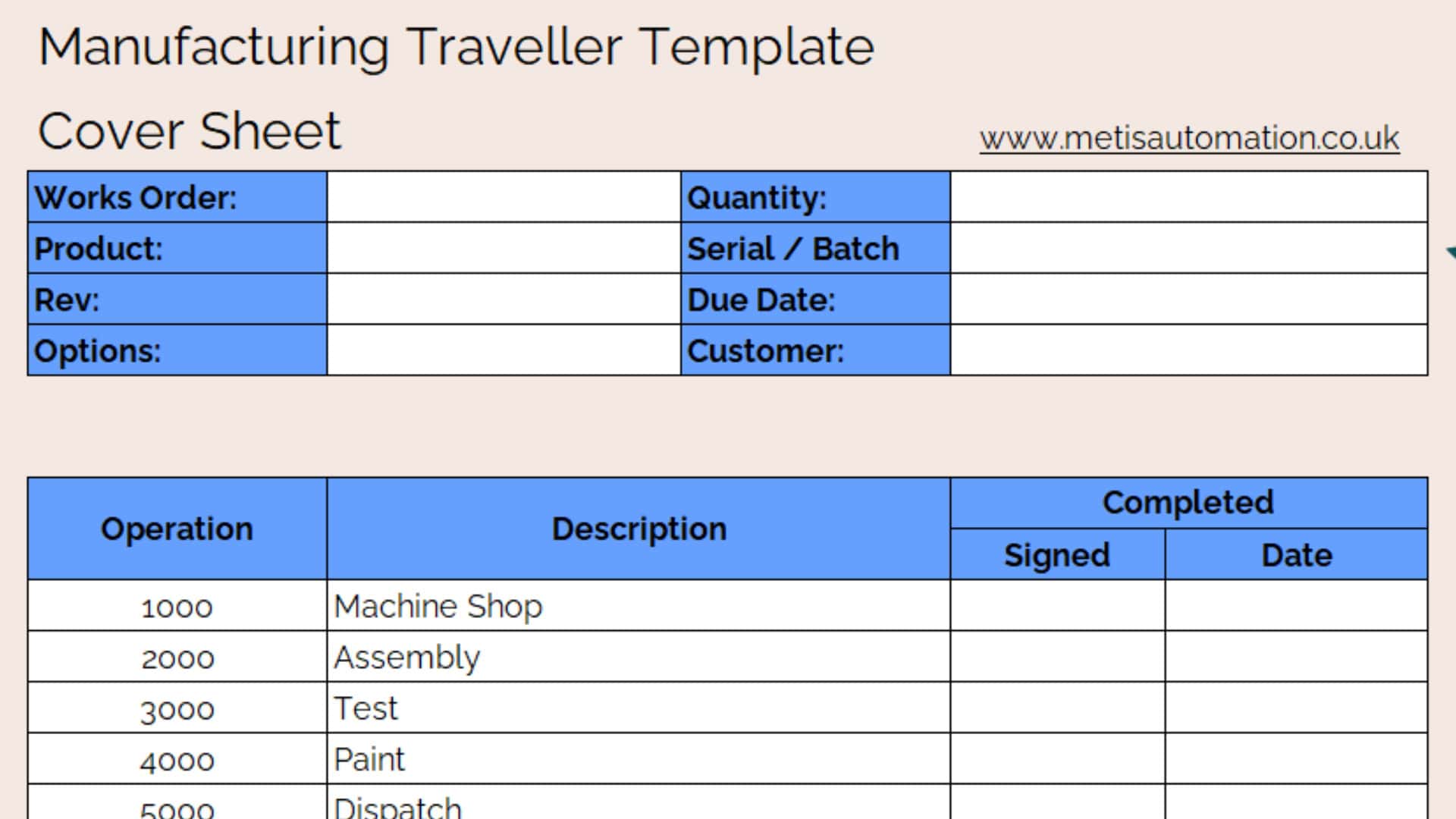
The manufacturing traveler, once a simple paper document, is undergoing a digital transformation. This evolution is not just about replacing pen-and-paper with electronic records; it’s about integrating the traveler into a sophisticated ecosystem of data, processes, and real-time communication. Manufacturers are recognizing the traveler’s potential for streamlining workflows, enhancing efficiency, and gaining crucial insights into production performance.
This transformation is fueled by the need for greater visibility, data-driven decision making, and seamless integration with existing enterprise systems. The digital traveler, with its ability to collect, analyze, and disseminate information, is playing a pivotal role in meeting these demands.
Emerging Trends in Manufacturing Traveler Technology
The manufacturing traveler is rapidly adopting cutting-edge technologies. Cloud-based platforms are enabling real-time access and collaboration across geographical locations. Integration with augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) systems allows for interactive visualization of data and processes. Furthermore, machine learning algorithms are being used to predict potential issues and optimize production schedules. These advancements are leading to more dynamic and adaptable manufacturing processes.
Integration of Manufacturing Travelers with Other Systems
Effective integration is critical for maximizing the traveler’s value. Digital travelers can seamlessly connect with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, providing real-time updates on inventory, orders, and production schedules. This synchronization streamlines communication and reduces data silos. Further integration with manufacturing execution systems (MES) provides comprehensive data about the production floor, including machine performance, material usage, and quality control metrics. This holistic view allows for more informed decision-making.
Use of Travelers in Automating Production Processes, Manufacturing traveler
Automation is key to optimizing manufacturing processes. Digital travelers can automate data collection, reducing manual errors and speeding up data entry. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) can be integrated to trigger automated actions based on traveler data, like adjusting machine parameters or initiating preventative maintenance. This level of automation ensures consistent quality and reduces downtime.
Data from Manufacturing Travelers for Analysis
The data collected by manufacturing travelers provides a wealth of information for analysis. Historical data can be used to identify trends, predict future performance, and optimize resource allocation. Real-time data can be used for proactive problem-solving, allowing manufacturers to address issues before they impact production. Data visualization tools integrated with the traveler system can transform complex data into easily digestible insights.
Role of Digital Travelers in Enhancing Communication and Collaboration
Digital travelers facilitate enhanced communication and collaboration. Real-time updates on production status can be shared with stakeholders across departments and geographically dispersed teams. This transparency fosters better communication and allows for faster problem-solving. Collaboration tools integrated with the traveler system enable team members to share insights, provide feedback, and collaborate on solutions.
Examples of Optimizing Processes using Digital Travelers
A manufacturer of automotive parts used a digital traveler system to track component movement throughout the production process. Real-time data revealed bottlenecks in the assembly line, enabling the company to reconfigure workflows and reduce production time by 15%. Another manufacturer in the aerospace industry leveraged digital travelers to improve quality control. The traveler system captured data on every stage of production, enabling the company to identify and rectify inconsistencies before they affected the final product.
Comparison of Traditional and Digital Manufacturing Travelers
| Feature | Traditional Travelers | Digital Travelers |
|---|---|---|
| Data Capture | Manual data entry, prone to errors, limited data points | Automated data collection, real-time updates, comprehensive data points |
| Accessibility | Limited access, primarily to those physically present | Remote access, accessible across devices and locations |
| Data Analysis | Limited data analysis capabilities, manual reporting | Real-time data analysis, predictive modeling, data visualization |
Key Considerations for Implementation

Manufacturing travelers are becoming increasingly vital in streamlining operations and enhancing efficiency within factories. However, successful implementation requires careful consideration of several key factors. A poorly planned implementation can lead to wasted resources and diminished productivity. Therefore, a thoughtful approach is crucial to realizing the full potential of these systems.
Implementing a manufacturing traveler system is not a simple “plug-and-play” process. It demands a thorough understanding of existing workflows, potential challenges, and the specific needs of the manufacturing environment. Careful planning and execution are paramount for a smooth transition and maximized return on investment.
Selecting a Manufacturing Traveler System
Choosing the right manufacturing traveler system is critical. Considerations include the specific needs of the manufacturing process, the volume of data to be tracked, and the types of information required. Factors such as scalability, integration capabilities, user-friendliness, and cost-effectiveness should be carefully evaluated. A system that is too complex or inflexible will hinder productivity, while one that is too basic may not capture the necessary details for effective decision-making. Prioritize a system that adapts to future needs and technological advancements.
Data Security and Privacy
Data security and privacy are paramount when using manufacturing travelers. Sensitive production data, employee information, and intellectual property need robust protection. Implementing strong encryption protocols, access controls, and regular security audits is crucial. Compliance with relevant regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA, is also essential. Organizations must have clear data handling policies and procedures in place to mitigate risks. Data breaches can lead to significant financial and reputational damage, highlighting the need for proactive measures.
Potential Challenges in Implementation
Implementing a new manufacturing traveler system can present various challenges. These include resistance to change from employees accustomed to existing methods, difficulties in integrating the system with legacy software, and ensuring seamless data transfer between different departments. Training needs to be adequately addressed, and proper support structures must be in place to guide employees through the transition. Adequate planning, clear communication, and comprehensive training programs can significantly mitigate these challenges.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may be hesitant to adopt new systems, potentially hindering smooth integration. Addressing these concerns with clear communication and demonstrating the benefits of the traveler system can help overcome this obstacle.
- Legacy System Integration: Integrating a new traveler system with existing software can be complex. A thorough assessment of compatibility issues and a phased implementation strategy can ease this transition.
- Data Transfer: Ensuring accurate and efficient data transfer between departments and systems is crucial for maintaining data integrity. A robust data migration plan will be necessary to avoid data loss or corruption.
Employee Training
Proper training is essential for employees using manufacturing travelers. Comprehensive training programs should cover the system’s functionalities, data entry procedures, and safety protocols. Clear instructions and practical demonstrations are crucial for ensuring employees can effectively use the system. Hands-on training, coupled with ongoing support, will empower users and maximize the system’s value.
System Integration
Integrating manufacturing travelers with existing systems is a crucial aspect of implementation. Careful planning is necessary to ensure smooth data flow between different departments and software applications. The integration process should be well-documented, and a dedicated team should oversee the transition. This ensures data accuracy and avoids disruptions in workflow.
- Data Mapping: Identify the corresponding data fields between the traveler system and existing systems. A detailed mapping document will guide the integration process and prevent data discrepancies.
- API Integration: Leveraging Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) for seamless data exchange between systems can improve efficiency and reduce manual intervention.
- Phased Approach: A phased integration approach, starting with a pilot program, allows for testing and refinement before full implementation.
Best Practices for Using Manufacturing Travelers
Implementing best practices will optimize the use of manufacturing travelers. These practices include maintaining accurate data entry, adhering to established procedures, and utilizing the system for real-time monitoring. Regular system maintenance and data backups are essential to ensure continued functionality and prevent data loss. Regular reviews of traveler data can provide insights into process inefficiencies, enabling proactive adjustments and improved production outcomes.
- Data Accuracy: Accurate data entry is crucial for reliable reporting and decision-making. Establish clear guidelines and implement quality control measures.
- Standardized Procedures: Establish standard operating procedures (SOPs) for using the traveler system to ensure consistency and accuracy across different departments and shifts.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Utilize the system for real-time monitoring of production processes, allowing for immediate identification and resolution of potential issues.
- Regular Maintenance: Scheduled maintenance of the system and data backups are vital to ensure its continued functionality and protect against data loss.
Illustrative Examples
Manufacturing travelers are not just a theoretical concept; they are actively transforming production lines in various industries. Their ability to streamline processes, reduce errors, and boost overall efficiency makes them a valuable tool for modern manufacturers. Real-world examples showcase the tangible benefits of implementing these systems.
Automotive Manufacturing
The automotive industry, known for its complex production processes, often benefits significantly from traveler systems. Consider a scenario where a car manufacturer produces several models simultaneously on a single assembly line. Each model requires a unique set of parts and procedures. A traveler system, meticulously designed with each model’s specifications, can precisely track the required components for each vehicle. This eliminates the risk of missing parts, reduces errors in assembly, and allows for efficient workflow management. The traveler system acts as a visual guide for the assembly line workers, ensuring each step is executed correctly and on time.
Electronics Manufacturing
The electronics industry demands precise and consistent quality control. A traveler system can be implemented to manage the various stages of assembly for intricate electronic components. Imagine a scenario where a mobile phone manufacturer assembles numerous components, each with specific tolerances and requirements. A traveler can track each step of the assembly process, ensuring the correct components are used, in the correct order, and with the precise specifications. This approach significantly reduces errors in component placement and improves the overall quality of the finished product. The visual traveler clearly identifies the required components for each assembly stage, ensuring no mistakes are made.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
The pharmaceutical industry operates under strict regulatory guidelines. A manufacturing traveler can effectively manage the different stages of drug production, from raw material handling to final packaging. Consider a pharmaceutical plant producing multiple batches of medication simultaneously. A traveler can track the specific materials used in each batch, along with the exact procedures followed during the production process. This detailed record-keeping is crucial for traceability and regulatory compliance. The traveler system, in this instance, can ensure that each batch meets stringent quality standards, eliminating the potential for errors or inconsistencies. The traveler clearly indicates the necessary steps for each batch, eliminating human errors in complex procedures.
Case Study: A Hypothetical Metal Fabrication Facility
A metal fabrication facility experienced significant challenges with production delays and errors in their cutting and shaping processes. They employed a traveler system to track the progress of each order through the different stages of production. This allowed them to identify bottlenecks in the process and optimize workflow. The travelers visually illustrated the sequence of operations, reducing errors in material handling and increasing efficiency. Initially, the facility experienced delays in completing orders due to miscommunication between departments and inconsistencies in work instructions. The introduction of travelers significantly reduced these problems, increasing productivity by 15% and decreasing errors by 20%. The implementation of a traveler system provided a clear visual representation of the production process, improving communication and collaboration among team members. The facility now effectively manages multiple orders simultaneously, delivering high-quality products on time and within budget.
Visual Representation: Assembly Line Traveler
A traveler, designed for a specific assembly line, consists of a laminated sheet with sequential stages of assembly depicted in a clear, step-by-step manner. Each stage is marked with a corresponding checklist box, which workers can check off as they complete each step. This system is color-coded, highlighting critical steps or potential error points. The traveler also includes the required parts, component identification numbers, and assembly instructions for each step. The traveler clearly illustrates the process to workers. The traveler is designed to be easily transported and updated as needed.
Real-World Problem and Solution
A textile manufacturer faced the problem of inconsistent dyeing times and variations in fabric quality. Workers were manually recording data, leading to errors and inefficiencies. Implementing a traveler system solved this problem. Each traveler, representing a specific fabric batch, included a schedule of dyeing times, temperature settings, and quality control checkpoints. Workers could easily follow the traveler, ensuring the correct procedures were consistently followed for each batch, leading to improved dyeing times and consistent fabric quality. The introduction of travelers eliminated inconsistencies, leading to significant improvement in quality and productivity.
Ever wondered what it’s like to be a manufacturing traveler? It’s a dynamic lifestyle, constantly on the move, and finding the right resources can be crucial. Navigating the complexities of travel nursing can be challenging, but finding the best cpa for travel nurses is equally important. This resource will help you make informed decisions for your next travel nursing adventure.
Ultimately, the right resources are key to a smooth and successful manufacturing traveler experience.
Manufacturing travelers often need specialized storage solutions, and a great example is the gigi pip hat travel case. This case, designed with the meticulous craftsmanship you’d expect from a quality manufacturer, is perfect for keeping your delicate hats safe and organized during your travels. Ultimately, these kinds of travel accessories highlight the importance of thoughtful design in the manufacturing traveler world.