The Suitability of QuickBooks for Personal Finances
QuickBooks, a popular accounting software primarily designed for businesses, can also be considered for managing personal finances. While its robust features are tailored for business needs, some individuals find its comprehensive capabilities beneficial for tracking income, expenses, and overall financial health. However, it’s crucial to understand its core functions and weigh the pros and cons before adopting it for personal use.
QuickBooks offers a range of functionalities that can be applied to personal finance management. These include transaction tracking, budgeting, reporting, and reconciliation. Understanding these core functions is key to determining if QuickBooks aligns with your financial management needs.
Core Functions of QuickBooks and Their Relation to Financial Management
QuickBooks’ core functions, when applied to personal finances, provide a structured approach to financial management. Each function contributes to a comprehensive understanding of your financial position.
- Transaction Tracking: This involves recording every financial transaction, including income (salary, investments) and expenses (bills, groceries, entertainment). QuickBooks allows for categorization of transactions, providing insights into spending habits. For example, you can categorize your grocery expenses as “Food” and your utility bills as “Utilities,” enabling you to track how much you spend in each category.
- Budgeting: QuickBooks allows users to create budgets based on income and expense categories. This feature helps in planning and controlling spending. You can set monthly budgets for different categories and track your actual spending against those budgets. For instance, you might budget $500 for groceries and then monitor your spending to ensure you stay within that limit.
- Reporting: QuickBooks generates various financial reports, such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. These reports provide a clear overview of your financial performance. For example, an income statement shows your income and expenses over a specific period, helping you determine your net income or loss.
- Reconciliation: This function involves comparing your bank statements with the transactions recorded in QuickBooks to ensure accuracy. This process helps identify any discrepancies and ensures that your records are up-to-date. Regularly reconciling your bank accounts is essential for maintaining accurate financial records.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using QuickBooks for Personal Finance
Using QuickBooks for personal finance presents both advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these aspects helps individuals make an informed decision about whether this software suits their needs.
- Advantages:
- Comprehensive Features: QuickBooks offers a wide array of features, providing detailed insights into your finances.
- Reporting Capabilities: The software generates various reports that provide a comprehensive overview of your financial situation.
- Accuracy: QuickBooks helps reduce errors and ensures accurate financial record-keeping.
- Scalability: If your financial needs evolve, QuickBooks can accommodate increased complexity.
- Disadvantages:
- Complexity: QuickBooks can be complex for users unfamiliar with accounting principles.
- Cost: The software requires a subscription, which can be expensive for personal use.
- Overkill: Many features may be unnecessary for simple personal finance needs.
- Learning Curve: Mastering the software requires time and effort.
Common Misconceptions About Using Accounting Software for Personal Use
There are several common misconceptions about using accounting software like QuickBooks for personal finance. Addressing these helps users make informed decisions.
- Misconception: Accounting software is only for businesses. While QuickBooks is primarily designed for businesses, its features can be adapted for personal finance management. The core functionalities of tracking income, expenses, and creating reports are beneficial for both business and personal use.
- Misconception: It’s too complicated for personal use. While QuickBooks has a steep learning curve, many users find that with some effort, they can navigate its features to manage their finances effectively. Online tutorials and resources can assist in learning the software.
- Misconception: It’s unnecessary if you already use a budgeting app. QuickBooks offers more advanced features than basic budgeting apps, such as detailed reporting and reconciliation. It can provide a more comprehensive view of your financial health.
- Misconception: It’s only useful for high-net-worth individuals. QuickBooks can benefit anyone seeking to gain a deeper understanding of their finances, regardless of their net worth. It helps in tracking spending, planning budgets, and making informed financial decisions.
Setting Up QuickBooks for Personal Use
QuickBooks, while designed for businesses, can be adapted for personal finance management. The initial setup is crucial for accurate tracking and reporting. This section details the process of creating a personal finance account in QuickBooks, including setting up categories and importing transactions.
Creating a Personal Finance Account in QuickBooks, Can i use quickbooks for personal finances
The process of setting up a personal finance account in QuickBooks involves several key steps. These steps ensure that your financial data is organized and readily accessible.
* Choosing the Right QuickBooks Version: Decide whether to use QuickBooks Online or QuickBooks Desktop. QuickBooks Online offers cloud-based access, while QuickBooks Desktop is installed on your computer. Choose the version that best suits your needs. QuickBooks Online often suits personal use due to its accessibility.
* Creating a New Company File: Start by creating a new company file. In QuickBooks, select “Create a New Company.”
* Selecting the Company Type: When prompted, choose “Other” or “Personal Finances” as the company type. This simplifies the setup process by providing a tailored starting point.
* Entering Basic Information: Enter your personal information, including your name and address. This information is used for reporting and identification purposes.
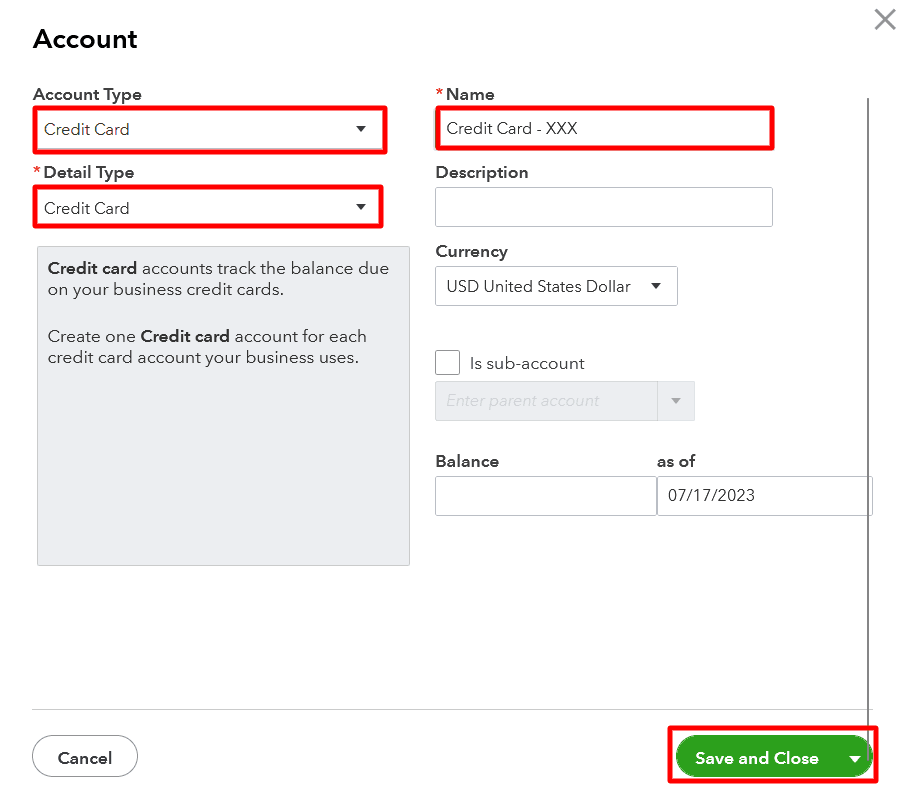
* Setting Up the Chart of Accounts: The Chart of Accounts is the backbone of your financial organization. You’ll be able to customize this later, but QuickBooks will offer a default chart based on the company type selected. You can edit this as needed.
* Linking Bank Accounts: Connect your bank accounts to QuickBooks. This allows for automatic transaction imports, saving time and reducing manual data entry.
Organizing Income and Expense Categories
Organizing income and expense categories is essential for tracking your spending and understanding your financial habits. A well-structured system allows you to generate insightful reports.
* Income Categories: Income categories represent all sources of money coming into your accounts. Examples include:
* Salary/Wages: Income from your primary employment.
* Investment Income: Earnings from investments like stocks or bonds.
* Freelance Income: Earnings from freelance work or side hustles.
* Interest Earned: Interest from savings accounts or other interest-bearing accounts.
* Gifts Received: Money received as gifts.
* Expense Categories: Expense categories represent where your money is being spent. Examples include:
* Housing: Rent/Mortgage, property taxes, and home maintenance.
* Utilities: Electricity, water, gas, and internet.
* Transportation: Car payments, gas, public transport, and car insurance.
* Food: Groceries, dining out, and takeout.
* Healthcare: Medical bills, insurance premiums, and prescriptions.
* Entertainment: Movies, concerts, and recreational activities.
* Personal Care: Haircuts, toiletries, and cosmetics.
* Debt Payments: Credit card payments, student loans, and other loans.
* Savings/Investments: Contributions to savings accounts, retirement accounts, or investment portfolios.
* Creating Categories in QuickBooks:
* Navigate to the “Chart of Accounts.”
* Click on “New” to create a new account.
* Select the account type (Income or Expense).
* Enter the category name and description.
* Specify any sub-categories if needed (e.g., “Groceries” under “Food”).
* Using Sub-categories: Sub-categories provide a more detailed breakdown of your spending. For example, under “Housing,” you might have sub-categories for “Rent,” “Mortgage Payment,” and “Property Taxes.” This level of detail provides more granular insights into your spending habits.
Importing Bank Transactions into QuickBooks
Importing bank transactions into QuickBooks automates the data entry process and ensures your financial records are up-to-date. The method of importing depends on whether you use QuickBooks Online or Desktop.
* Importing with QuickBooks Online:
* Connecting Your Bank: Connect your bank accounts to QuickBooks Online. This allows QuickBooks to automatically download transactions.
* Downloading Transactions: If your bank isn’t supported for direct connection, you can download a CSV, QBO, or OFX file from your bank’s website.
* Importing the File: In QuickBooks Online, go to the “Transactions” or “Banking” section and select “File Upload.”
* Mapping Transactions: Map the transactions to the correct accounts and categories.
* Importing with QuickBooks Desktop:
* Downloading Transactions: Download a QBO or OFX file from your bank’s website.
* Importing the File: In QuickBooks Desktop, go to “File” > “Utilities” > “Import” > “Bank Feeds.”
* Selecting the File: Choose the downloaded file.
* Mapping Transactions: Review and map the transactions to the correct accounts and categories.
* Manual Entry (If Necessary): If your bank doesn’t support downloads or you have manual transactions, you can enter them directly into QuickBooks.
* Go to “Banking” > “Enter Transactions.”
* Enter the date, amount, payee, and category.
* Save the transaction.
* Reconciling Your Accounts: Regularly reconcile your bank accounts with your QuickBooks records. This ensures the accuracy of your data and helps identify any discrepancies. Reconciling typically involves comparing your bank statement with the transactions in QuickBooks.
Core Features and Their Applications
QuickBooks offers several core features that can be adapted for personal finance management, streamlining the process of tracking income, expenses, and overall financial health. These features allow users to gain insights into their spending habits, create budgets, and generate financial reports, providing a comprehensive view of their finances.
Using the “Banking” Feature to Categorize Transactions
The “Banking” feature in QuickBooks is a cornerstone for organizing and understanding personal finances. It allows users to import transactions from bank and credit card accounts and then categorize them appropriately.
To categorize transactions using the “Banking” feature:
- Connect Your Accounts: Begin by connecting your bank and credit card accounts to QuickBooks. This process typically involves entering your online banking credentials, and QuickBooks will securely download your transaction history. The exact steps will depend on your financial institution.
- Review and Categorize Transactions: Once the transactions are imported, they will appear in the “Banking” section. QuickBooks often suggests categories based on the payee or transaction description. Review these suggestions and select the correct category for each transaction. For example, a purchase from “Starbucks” might be categorized as “Food & Dining,” while a payment to “Mortgage Company” would be categorized as “Housing.”
- Create New Categories (If Needed): If a transaction doesn’t fit into an existing category, you can create a new one. Go to the “Chart of Accounts” (usually found under “Accounting”) and click “New.” Select the account type (e.g., “Expense”) and enter the category name (e.g., “Entertainment”).
- Use Rules for Automation: QuickBooks allows you to set up rules to automatically categorize transactions based on certain criteria, such as the payee or description. This can save time and ensure consistency in your categorization. For example, you can create a rule to automatically categorize all transactions from “Amazon” as “Shopping.”
- Review and Reconcile: Regularly review the categorized transactions to ensure accuracy. Reconcile your QuickBooks accounts with your bank statements each month to identify any discrepancies and ensure all transactions are accounted for.
Generating Reports for Personal Finance Tracking
QuickBooks’ reporting capabilities are invaluable for analyzing your financial data and making informed decisions. Users can generate a variety of reports to track income, expenses, and overall financial performance.
Here are some key reports and how to generate them:
- Income Statement (Profit and Loss): This report summarizes your income and expenses over a specific period. To generate an income statement:
- Go to the “Reports” menu.
- Select “Profit & Loss.”
- Choose the date range you want to analyze (e.g., “This Year,” “Last Month,” or a custom range).
- Review the report to see your total income, expenses, and net profit or loss.
This report helps you understand your profitability and identify areas where you might be overspending or where your income is coming from.
- Balance Sheet: The balance sheet provides a snapshot of your assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. To generate a balance sheet:
- Go to the “Reports” menu.
- Select “Balance Sheet.”
- Choose the as-of-date you want to analyze.
- Review the report to see your assets (e.g., cash, investments), liabilities (e.g., loans, credit card debt), and equity (net worth).
The balance sheet helps you assess your financial position and track your net worth.
- Cash Flow Statement: While QuickBooks doesn’t have a pre-built cash flow statement specifically designed for personal finance, you can create a custom report that approximates it. This statement tracks the movement of cash in and out of your accounts.
- Go to the “Reports” menu.
- Select “Transaction Detail by Account.”
- Customize the report to show all transactions for your bank accounts and credit cards.
- Filter the report by transaction type (e.g., “Check,” “Deposit,” “Credit Card Charge”).
- Review the report to see the cash inflows (e.g., income) and cash outflows (e.g., expenses).
This report helps you understand where your cash is coming from and where it’s going.
- Budget vs. Actual Report: This report compares your budgeted amounts with your actual spending for each category.
- Go to the “Reports” menu.
- Select “Budget vs. Actual.”
- Choose the budget you want to compare.
- Select the date range.
- Review the report to see how your actual spending compares to your budget.
This report helps you identify areas where you are overspending and make adjustments to your budget.
Creating a Budget within QuickBooks
Budgeting is a critical aspect of personal finance, and QuickBooks offers tools to create and manage budgets effectively. Setting up a budget helps you plan your spending, track your progress, and achieve your financial goals.
To create a budget within QuickBooks:
- Access the Budgeting Tools: Go to the “Budget” section (usually found under “Planning & Budgeting” or similar).
- Create a New Budget: Click “Create New Budget.”
- Select the Budget Period: Choose the budget period (e.g., monthly, quarterly, annually).
- Select the Account Type: Choose whether you want to budget for “Income & Expenses” or “Expenses Only.”
- Set Budget Amounts for Categories:
- QuickBooks will display a list of your income and expense categories.
- Enter the budgeted amount for each category for the chosen period. You can either enter amounts manually or use data from previous periods as a starting point.
- For example, if your average monthly spending on groceries is $400, enter $400 in the “Groceries” category.
- If you have irregular income, such as from freelance work, estimate the amount you expect to earn each month and enter it in the corresponding income category.
- Customize the Budget:
- You can customize the budget by adding or removing categories, as needed.
- You can also choose to budget for specific classes or locations if you want to track spending by different projects or areas of your life.
- Save the Budget: Once you have entered all the budget amounts, save the budget.
- Track Your Progress: Regularly review your budget and compare it to your actual spending using the “Budget vs. Actual” report. Make adjustments to your budget as needed to stay on track.
By following these steps, individuals can effectively leverage QuickBooks’ core features to manage their personal finances, gain valuable insights, and achieve their financial goals.
Tracking Income and Expenses
Accurately tracking income and expenses is crucial for effective personal financial management, providing a clear picture of where your money comes from and where it goes. This data forms the foundation for budgeting, identifying areas for savings, and making informed financial decisions. QuickBooks offers robust tools for managing both income and expenses, enabling users to gain valuable insights into their financial health.
Entering Income Sources
Managing income effectively involves categorizing and recording all sources of revenue. This ensures a comprehensive view of your financial inflows, enabling better financial planning.
Income sources can include:
- Salary or Wages: This is the primary source of income for most individuals. When entering salary or wages, ensure you record the gross amount before any deductions.
- Freelance or Contract Work: If you work as a freelancer or contractor, track each payment received. Include the date, client name, and the amount.
- Investment Income: This includes dividends, interest earned from savings accounts, and profits from selling investments. QuickBooks allows you to categorize these separately.
- Rental Income: If you own rental properties, record the income received from tenants. Include the property address and the date of the payment.
- Other Income: This category covers any other sources of income, such as gifts, royalties, or any miscellaneous earnings.
For example, if you receive a dividend payment of $100 from a stock investment, you would create a new income transaction in QuickBooks. You would select the date the dividend was received, the account where the money was deposited (e.g., checking account), and categorize it as “Investment Income.” You can further specify the source, such as the name of the company that issued the dividend.
Recording Expenses and Payment Methods
Accurately recording expenses is equally important for understanding your spending habits and identifying areas where you can potentially reduce costs. QuickBooks supports various payment methods, ensuring you can track all transactions effectively.
The different methods for recording expenses include:
- Cash: For cash transactions, record the date, the vendor, the amount, and the expense category.
- Checks: When paying by check, enter the check number, date, vendor, amount, and the expense category.
- Credit Cards: Import credit card transactions directly into QuickBooks or manually enter them. Specify the date, vendor, amount, and expense category.
- Debit Cards: Similar to credit cards, track debit card transactions by entering the date, vendor, amount, and expense category.
- Online Payments (e.g., PayPal, Venmo): Record the date, the vendor, the amount, and the expense category for online payments.
For instance, if you pay your monthly utility bill of $150 using a credit card, you would create a new expense transaction in QuickBooks. You would select the date the payment was made, the credit card account, the vendor (e.g., Utility Company), the amount, and categorize it as “Utilities.” QuickBooks will then track this expense, which will be reflected in your expense reports.
Tracking Investments and Assets
Tracking investments and assets within QuickBooks provides a comprehensive view of your net worth and helps you monitor the performance of your investments. This includes stocks, bonds, real estate, and other valuable possessions.
The process for tracking investments and assets includes:
- Creating Asset Accounts: Set up separate accounts for each type of asset, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and savings accounts.
- Recording Investment Purchases: When you purchase an investment, record the transaction, including the date, the asset account, the amount, and the details of the investment (e.g., stock ticker symbol).
- Tracking Investment Sales: When you sell an investment, record the transaction, including the date, the asset account, the amount received, and the gain or loss.
- Monitoring Dividends and Interest: Record any dividends or interest earned from your investments as income.
- Valuing Assets: Regularly update the value of your assets, such as real estate or stocks, to reflect their current market value.
For example, if you purchase 100 shares of a stock for $5,000, you would create a new transaction in QuickBooks. You would select the date of the purchase, debit the investment account (e.g., Stocks), credit the checking account (if purchased with cash), enter the amount, and specify the stock name and ticker symbol. Regularly reviewing and updating these records helps in understanding the true value of your portfolio.
Reporting and Analysis: Can I Use Quickbooks For Personal Finances
Analyzing financial data through reports is crucial for effective personal financial planning and achieving financial goals. QuickBooks offers a range of reporting tools that provide insights into income, expenses, and overall financial health. Understanding how to generate, interpret, and utilize these reports allows individuals to make informed decisions about their finances.
The ability to generate and analyze reports is a significant advantage of using QuickBooks for personal finance. This section focuses on the key reports that are most beneficial for personal financial planning and provides guidance on how to interpret them for informed decision-making.
Key Reports Useful for Personal Financial Planning and Review
Several reports in QuickBooks are particularly useful for understanding and managing personal finances. These reports provide different perspectives on financial data, allowing for a comprehensive review of income, expenses, and overall financial performance. Regularly reviewing these reports can help individuals stay on track with their financial goals and identify areas for improvement.
- Profit and Loss (Income Statement): This report summarizes income and expenses over a specific period. It helps determine profitability by showing whether income exceeds expenses.
- Balance Sheet: The balance sheet provides a snapshot of assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. It shows what an individual owns (assets) and owes (liabilities), along with their net worth (equity).
- Cash Flow Statement: This report tracks the movement of cash in and out of an individual’s accounts over a period. It helps understand where cash is coming from and where it’s being spent.
- Budget vs. Actual: This report compares budgeted amounts for income and expenses with actual amounts. It highlights variances and helps identify areas where spending is over or under budget.
- Transaction Detail Report: This report provides a detailed list of all transactions, allowing for a thorough review of specific transactions and identifying potential errors or discrepancies.
Comparison of Standard QuickBooks Reports with Personal Finance Needs
QuickBooks provides a variety of standard reports, but the suitability of these reports for personal finance may vary. Some reports are directly applicable, while others may require customization or interpretation to meet specific needs. The table below compares standard QuickBooks reports with those typically needed for personal finance, outlining their purpose and benefits.
| Report Name | Purpose | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Profit and Loss (Income Statement) | Summarizes income and expenses over a period, showing profitability. |
|
| Balance Sheet | Provides a snapshot of assets, liabilities, and net worth at a specific point in time. |
|
| Cash Flow Statement | Tracks the movement of cash in and out of accounts. |
|
| Budget vs. Actual | Compares budgeted amounts with actual spending. |
|
| Transaction Detail Report | Provides a detailed list of all transactions. |
|
Interpreting Reports for Informed Decision-Making
Understanding how to interpret financial reports is essential for making informed financial decisions. This involves analyzing the data presented in the reports and using the insights gained to adjust financial strategies. Here are some examples of how to interpret key reports for informed decision-making:
- Profit and Loss: If the report shows a consistent loss (expenses exceeding income), it signals a need to reduce expenses or increase income. For example, if a report shows monthly expenses exceeding income by $500, an individual might explore ways to cut spending, such as reducing dining out or entertainment costs, or consider taking on a side hustle to increase income.
- Balance Sheet: Analyzing the balance sheet can help assess net worth and debt levels. If the report reveals a high level of debt, it may be necessary to prioritize debt repayment. Consider a scenario where an individual has a mortgage and credit card debt. If the credit card debt is accumulating interest at a higher rate, they might choose to allocate extra funds to pay off the credit card debt first.
- Cash Flow Statement: Reviewing the cash flow statement can reveal spending patterns and identify areas where cash is being mismanaged. If the report shows that a significant portion of cash is being spent on non-essential items, it might be a sign to re-evaluate spending habits. For example, if a significant amount of cash is flowing out for subscriptions, the individual might decide to cancel some subscriptions.
- Budget vs. Actual: Comparing budgeted and actual spending helps identify variances and potential areas for improvement. If the report shows that spending in a specific category consistently exceeds the budget, it indicates a need to adjust the budget or reduce spending in that category. If the entertainment budget is consistently overspent, the individual might consider reducing the amount spent on entertainment or finding cheaper alternatives.
- Transaction Detail Report: This report allows for detailed analysis of individual transactions. If the report reveals frequent and unnecessary transactions, it signals a need to reassess spending habits. For example, if a transaction detail report shows multiple small purchases at a convenience store each week, the individual might consider packing lunches or snacks to avoid these impulse buys.
Advanced Techniques and Customization
QuickBooks offers advanced features and customization options that allow users to tailor the software to their specific personal finance needs, going beyond basic income and expense tracking. These techniques enhance the depth and accuracy of financial management, providing a more comprehensive view of your financial health.
Using Classes and Locations for Detailed Tracking
Classes and locations are powerful tools within QuickBooks that allow for detailed categorization and analysis of financial transactions. They provide a way to segment your finances beyond the standard categories, giving you greater insight into where your money is coming from and going.
To understand the application of classes and locations, consider these points:
- Classes: Classes categorize transactions by different aspects, such as projects, departments, or types of activities. For example, if you have multiple side hustles, you can create a class for each to track the income and expenses associated with each one separately. This allows you to easily see which side hustle is most profitable.
- Locations: Locations categorize transactions based on where they occur. This is particularly useful if you have multiple properties or business locations. You can track income and expenses related to each location independently.
- Application in Personal Finance: While primarily designed for businesses, classes and locations can be adapted for personal use. Imagine you are renovating your home. You can create a class for “Home Renovation” and then sub-classes for different rooms (e.g., “Kitchen,” “Bathroom”). You can then assign expenses related to each room to the corresponding sub-class.
- Reporting: QuickBooks allows you to run reports filtered by class or location. This provides a clear breakdown of financial performance for each category or location. You can analyze which side hustles are most profitable, the cost of renovating each room in your house, or the income generated from different rental properties.
By utilizing classes and locations, you can gain a much deeper understanding of your financial activities and make more informed decisions.
Reconciling Bank Accounts in QuickBooks
Reconciling your bank accounts in QuickBooks is a critical step in maintaining accurate financial records. It involves comparing your QuickBooks transactions with your bank statement to ensure they match. This process helps identify errors, fraud, and ensures that your financial data is up-to-date.
Here’s a procedure for reconciling bank accounts:
- Gather Your Bank Statement: Obtain your bank statement for the period you are reconciling. This is usually a monthly statement.
- Open the Reconcile Window in QuickBooks: In QuickBooks, navigate to the “Banking” menu and select “Reconcile.”
- Select the Account: Choose the bank account you are reconciling from the dropdown menu.
- Enter the Ending Balance: Enter the ending balance from your bank statement in the “Ending Balance” field.
- Enter the Ending Date: Enter the date of your bank statement in the “Ending Date” field.
- Enter Service Charges and Interest: If your bank statement shows any service charges or interest earned, enter them in the appropriate fields. QuickBooks will automatically create the necessary transactions.
- Mark Cleared Transactions: Compare the transactions on your bank statement with the transactions in QuickBooks. Check off each transaction that appears on both the statement and in QuickBooks.
- Review the Difference: QuickBooks will calculate the difference between the ending balance and the cleared transactions. The goal is for the difference to be zero.
- Investigate Discrepancies: If the difference is not zero, carefully review the transactions to identify any discrepancies. Common issues include:
- Missing transactions in QuickBooks.
- Incorrect transaction amounts.
- Duplicate transactions.
- Make Adjustments: Once you identify the discrepancies, make the necessary adjustments in QuickBooks. This might involve adding missing transactions, correcting amounts, or deleting duplicates.
- Reconcile: Once the difference is zero, click the “Reconcile” button. QuickBooks will then record the reconciliation.
Regular reconciliation ensures the accuracy of your financial records, enabling you to make informed financial decisions.
Customizing QuickBooks for Specific Personal Finance Needs
QuickBooks offers several customization options that allow you to tailor the software to your unique personal finance needs. This customization enhances the software’s utility, enabling more precise tracking and reporting of your financial situation.
Here are steps to customize QuickBooks for specific personal finance needs:
- Define Your Needs: Before customizing QuickBooks, clearly define your specific financial goals and the information you want to track. For example, do you want to track debt, net worth, or specific investment accounts?
- Customize the Chart of Accounts: The Chart of Accounts is the backbone of your financial tracking. Add or modify accounts to reflect your specific needs.
- Tracking Debt: Create liability accounts for each type of debt (e.g., “Credit Card Debt,” “Student Loan”).
- Tracking Net Worth: Create asset accounts for all your assets (e.g., “Checking Account,” “Savings Account,” “Investments”) and liability accounts for all your debts.
- Customize Income and Expense Categories: Adjust the income and expense categories to align with your spending habits. For instance, create categories like “Groceries,” “Dining Out,” or “Entertainment” to track spending patterns.
- Set Up Memorized Transactions: Memorized transactions can automate recurring transactions, such as rent or mortgage payments. This saves time and reduces the risk of errors.
- Create Custom Reports: QuickBooks offers various report templates, but you can also create custom reports to analyze your finances.
- Debt Tracking Report: Create a report that shows your outstanding debt balances, interest rates, and payment schedules.
- Net Worth Report: Generate a report that summarizes your assets, liabilities, and net worth over time.
- Utilize Classes and Locations (as discussed previously): Use classes and locations to further categorize transactions, such as tracking expenses related to specific projects or rental properties.
- Consider Third-Party Integrations: Explore third-party apps that integrate with QuickBooks to enhance its functionality. Some apps specialize in budgeting, debt management, or investment tracking.
By customizing QuickBooks, you create a personalized financial management tool that effectively tracks your finances and supports your financial goals.
Comparison with Alternatives
Choosing the right personal finance management tool is crucial for effective budgeting, tracking, and financial planning. While QuickBooks offers a robust solution, several other options cater to different needs and preferences. Understanding these alternatives, along with the benefits and drawbacks of different approaches, empowers individuals to make informed decisions aligned with their financial goals.
Comparing Personal Finance Software Options
Numerous personal finance software options are available, each with unique features, pricing structures, and target users. The following table provides a comparison of some popular choices, highlighting their key differences.
| Software | Price | Key Features | Target User |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mint | Free (with optional premium features) | Budgeting, expense tracking, bill payment, credit score monitoring, investment tracking, financial insights. | Individuals seeking a user-friendly, all-in-one solution for managing finances, especially those new to budgeting. |
| YNAB (You Need A Budget) | Subscription-based | Budgeting based on the “envelope” system, goal tracking, debt payoff planning, detailed reporting, bank account syncing. | Individuals committed to active budgeting and those looking to change their spending habits through a proactive approach. |
| Personal Capital | Free (with optional premium features) | Net worth tracking, investment analysis, retirement planning tools, budgeting, expense tracking, financial dashboards. | Individuals focused on investment management and retirement planning, seeking a comprehensive view of their financial portfolio. |
| Quicken | Subscription-based | Budgeting, expense tracking, bill payment, investment tracking, tax planning, reporting, customizable features. | Individuals seeking a feature-rich solution with advanced financial planning capabilities and investment tracking, often with more complex financial situations. |
| PocketGuard | Freemium (paid plans available) | Budgeting based on “safe-to-spend” calculations, expense tracking, bill tracking, debt management. | Individuals looking for a simple and automated budgeting tool that helps them understand their spending habits and available funds. |
Pros and Cons of Spreadsheets vs. QuickBooks
Spreadsheets, such as Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets, offer a flexible, customizable approach to personal finance management. QuickBooks, on the other hand, provides a more structured and integrated experience. Both have their advantages and disadvantages.
- Spreadsheets:
- Pros: Highly customizable, allowing users to create a system tailored to their specific needs; free or low-cost; provides a deep understanding of personal finances as the user manually enters and categorizes data; does not require internet access.
- Cons: Requires manual data entry, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors; lacks automated features like bank account syncing; requires a high degree of financial literacy to set up and maintain effectively; reporting and analysis can be complex to create.
- QuickBooks:
- Pros: Automates many tasks, such as bank account syncing and transaction categorization; offers robust reporting and analysis tools; provides a more structured approach to financial management; scales well for more complex financial needs.
- Cons: Can be more expensive than free spreadsheet options; may have a steeper learning curve for beginners; the features can be overwhelming for individuals with simple financial needs; less flexible than spreadsheets in terms of customization.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Free vs. Paid Personal Finance Software
The choice between free and paid personal finance software often hinges on individual needs, budget constraints, and the desired level of functionality. Both options offer distinct benefits and drawbacks.
- Free Software:
- Advantages: No upfront cost; accessible to anyone regardless of financial situation; often includes essential features like budgeting and expense tracking; a good starting point for individuals new to personal finance management.
- Disadvantages: May contain advertisements; limited features compared to paid versions; data security concerns if the provider isn’t reputable; often lacks advanced reporting and analysis tools; may have limited customer support.
- Paid Software:
- Advantages: More features and functionalities, such as advanced reporting, investment tracking, and bill payment; often includes enhanced security features; provides better customer support; generally ad-free; more frequent updates and improvements.
- Disadvantages: Requires a recurring subscription fee; may be more complex to use, especially for beginners; some features may be unnecessary for individuals with simple financial needs.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Navigating QuickBooks for personal finance isn’t always smooth sailing. Users often encounter hurdles, from data import glitches to the complexities of data management. This section addresses common problems and provides practical solutions to ensure a more efficient and user-friendly experience. Understanding these challenges and implementing the suggested remedies can significantly improve your financial management journey.
Troubleshooting Transaction Import Errors
Importing transactions, whether from banks or other sources, can sometimes lead to errors. These errors can disrupt your financial tracking, and knowing how to resolve them is crucial.
Can i use quickbooks for personal finances – Here are some common import issues and how to address them:
- Incorrect File Format: QuickBooks supports specific file formats like .QBO, .QFX, and CSV. Using an incompatible format is a frequent cause of import failures.
- Duplicate Transactions: Importing the same transactions multiple times can inflate your data and skew your reports.
- Character Encoding Issues: Incorrect character encoding, particularly with special characters, can corrupt data during import.
- Incorrect Account Mapping: If your bank feed or import file doesn’t properly link to the right accounts, transactions will be categorized incorrectly.
- Connection Problems: Bank feed connectivity issues can cause intermittent import problems.
Solution: Verify the file format matches QuickBooks’ supported types. If necessary, convert the file to a compatible format. For example, many banks offer CSV downloads, which often need minimal formatting before import. Review your bank’s or financial institution’s instructions on file formats for QuickBooks.
While QuickBooks isn’t ideal for basic personal budgeting, it can be used. However, when considering larger financial undertakings, such as obtaining asset financing for a car or home, its more complex features become less user-friendly for tracking personal finances. Ultimately, for personal use, simpler tools often provide a better experience than QuickBooks.
Solution: QuickBooks often detects and prevents duplicate imports, but manually reviewing transactions is still necessary. After importing, carefully compare the imported data with existing records. If duplicates exist, delete the redundant entries.
While QuickBooks isn’t ideal for personal finance tracking, it excels in business accounting. For those seeking financing for home improvements, like a new roof, exploring a roofing company that finances can be a smart move. However, if you’re managing personal budgets, other tools are generally better suited than QuickBooks.
Solution: Ensure the CSV file is saved with UTF-8 encoding. If you’re manually entering data, be mindful of special characters. QuickBooks may not correctly interpret certain characters, leading to import errors.
Solution: When setting up bank feeds or importing, double-check the account mapping. Ensure that transactions are assigned to the correct expense, income, or asset accounts. Review and adjust the account mapping settings within QuickBooks as needed.
Solution: Check your internet connection and the status of your bank’s server. If the problem persists, try disconnecting and reconnecting your bank feed within QuickBooks. Contact your bank or QuickBooks support if the problem is ongoing.
Managing and Backing Up QuickBooks Data
Protecting your financial data is paramount. Implementing a robust data management and backup strategy safeguards against data loss due to hardware failures, software corruption, or accidental deletion.
Effective data management and backup strategies involve:
- Regular Backups: Back up your QuickBooks data frequently.
- Data Verification: Periodically verify your QuickBooks data.
- Data File Location: Store your QuickBooks data file in a safe and accessible location.
- Password Protection: Secure your QuickBooks file with a strong password.
- User Access Controls: If multiple people use QuickBooks, set up user access controls.
Solution: QuickBooks allows for both local and online backups. Set up automatic backups to a local drive, external hard drive, or cloud storage service. Consider backing up your data at least weekly, or more frequently if you have significant transaction activity. You can access the backup feature under the “File” menu.
Solution: QuickBooks includes a “Verify Data” utility. This tool checks for data integrity issues. If errors are found, use the “Rebuild Data” utility to repair the file. Access these tools under the “File” menu, then “Utilities.”
Solution: Avoid storing the data file directly on your system drive (C:\) unless necessary. Instead, save it to a separate drive or external storage. This helps to isolate your financial data from potential system failures. Consider using a folder structure that clearly identifies your data files.
Solution: Set a password for your QuickBooks file to prevent unauthorized access. Regularly change your password and keep it secure. Consider using a password manager to securely store your password.
Solution: QuickBooks allows you to create different user roles with varying levels of access. This helps to restrict sensitive financial information and prevent accidental changes. Assign roles based on the user’s responsibilities.
Illustrative Examples and Case Studies
Understanding how QuickBooks can be applied in real-world scenarios provides valuable insight into its practical utility. This section explores specific use cases, offering tangible examples of how individuals and families leverage QuickBooks to manage their finances effectively. We will examine a family managing household finances, a freelancer separating personal and business accounts, and the creation of a sample budget tailored to a specific lifestyle.
Family Financial Management with QuickBooks
Many families find themselves needing to track their income and expenses to achieve their financial goals. QuickBooks offers tools to manage these aspects effectively.
For example, consider the Miller family, comprising two working parents and two children. Their financial goals include saving for their children’s college education, paying off their mortgage, and taking an annual family vacation. Their income consists of the parents’ combined salaries, totaling $120,000 annually, and occasional side-hustle income of around $5,000 per year. Their primary expenses include:
- Mortgage payments: $2,500 per month ($30,000 annually).
- Groceries: $800 per month ($9,600 annually).
- Utilities: $400 per month ($4,800 annually).
- Transportation: $500 per month ($6,000 annually).
- Childcare: $1,000 per month ($12,000 annually).
- Other expenses, such as entertainment, clothing, and healthcare, total approximately $2,000 per month ($24,000 annually).
The Millers utilize QuickBooks to track their income and expenses. They categorize their expenses meticulously, creating categories for each expense type. They use the “Banking” features to import bank transactions, and manually enter cash transactions. They set up budgets within QuickBooks, comparing their actual spending against budgeted amounts to identify areas where they can cut costs. The “Reports” feature allows them to generate monthly and annual financial reports, providing a clear picture of their financial health. They regularly review these reports to monitor their progress toward their financial goals, making adjustments as needed. They can see at a glance how much they are saving each month and adjust their spending accordingly. This data helps them make informed decisions about their finances, enabling them to stay on track with their goals.
Freelancer’s Financial Separation
Freelancers often juggle both personal and business finances, making it crucial to maintain a clear separation. QuickBooks is a valuable tool for achieving this.
Consider Sarah, a freelance graphic designer. Her income streams include:
- Client invoices: $60,000 annually.
- Royalties from stock images: $5,000 annually.
Her business expenses include:
- Software subscriptions: $2,000 annually.
- Website hosting: $500 annually.
- Marketing and advertising: $1,000 annually.
- Office supplies: $300 annually.
- Home office expenses (allocated based on square footage): $2,000 annually.
Sarah uses QuickBooks to create separate accounts for her personal and business finances. She sets up two bank accounts, one for personal and one for business. She tracks all business income and expenses in the business account. QuickBooks allows her to generate profit and loss statements, which provide a clear view of her business profitability. She can easily see her revenue, expenses, and net profit. This information is essential for tax purposes, as it helps her accurately report her business income and deductions. She also uses QuickBooks to invoice clients, track payments, and manage her accounts receivable. This streamlined process saves her time and ensures she gets paid promptly. Sarah can also use QuickBooks to forecast future earnings and plan for taxes, ensuring financial stability and compliance.
Sample Budget Creation for a Specific Lifestyle
Creating a budget tailored to a specific lifestyle is essential for effective financial management. QuickBooks provides the tools to create and manage such budgets.
Let’s create a sample budget for a single individual living in a mid-sized city, with a comfortable lifestyle. This individual, let’s call him David, earns an annual salary of $75,000. His financial goals include saving for a down payment on a house, traveling annually, and building an emergency fund. His estimated monthly expenses are as follows:
| Expense Category | Monthly Amount |
|---|---|
| Rent/Mortgage | $2,000 |
| Utilities | $250 |
| Groceries | $500 |
| Transportation (car payment, insurance, gas) | $400 |
| Entertainment | $300 |
| Dining Out | $200 |
| Clothing | $100 |
| Health Insurance | $300 |
| Personal Care | $50 |
| Internet/Phone | $100 |
| Debt Payments (student loans, etc.) | $300 |
| Savings (down payment, emergency fund) | $1,000 |
| Total Expenses | $5,500 |
David can create this budget in QuickBooks. He can set up each expense category and enter the budgeted amount for each. He can then track his actual spending each month and compare it to the budgeted amounts. If he finds that he is overspending in certain areas, he can adjust his budget accordingly. For example, if he is spending more than $300 per month on entertainment, he might choose to reduce his spending on dining out or other entertainment activities. This process allows David to stay on track with his financial goals, ensuring he saves enough for his down payment, emergency fund, and annual travel.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Protecting your financial data is paramount when using any software, and QuickBooks is no exception. Understanding the security measures in place and adopting best practices is crucial for safeguarding your personal financial information. This section explores the security features of QuickBooks, offers practical advice for maintaining data security, and emphasizes the importance of software updates.
QuickBooks Security Measures
QuickBooks employs several security measures to protect user data. These measures are designed to provide a secure environment for managing your finances.
- Data Encryption: QuickBooks uses data encryption to protect your financial information both in transit and at rest. This means that your data is scrambled and unreadable to unauthorized individuals, making it difficult for hackers to access your sensitive financial details. Intuit, the company behind QuickBooks, utilizes robust encryption algorithms to secure your data.
- User Authentication: QuickBooks requires users to authenticate their identity through strong passwords and multi-factor authentication (MFA). MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification method, such as a code sent to your mobile device, in addition to your password. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if your password is compromised.
- Role-Based Access Control: QuickBooks allows you to set up different user roles with varying levels of access. This means you can control who can view, edit, or delete financial data. This feature is particularly useful if you share your QuickBooks file with other individuals, such as a bookkeeper or accountant. For example, you might grant your accountant full access while limiting your assistant to view-only access to certain reports.
- Secure Data Centers: Intuit stores QuickBooks data in secure data centers with robust physical and electronic security measures. These data centers are monitored 24/7 and employ measures such as biometric scanners, surveillance cameras, and redundant power supplies to protect your data from physical threats and outages.
- Regular Security Audits: Intuit conducts regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities in its systems. These audits help to ensure that QuickBooks remains secure and that your data is protected against evolving threats.
Best Practices for Safeguarding Personal Financial Information
Implementing best practices significantly enhances the security of your financial data within QuickBooks. These practices help mitigate risks and protect your sensitive information.
- Use Strong Passwords: Create strong, unique passwords for your QuickBooks account. A strong password should be at least 12 characters long and include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid using easily guessable information such as your name, birthdate, or common words.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Always enable MFA for your QuickBooks account. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification method, such as a code sent to your mobile device, in addition to your password. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
- Regularly Back Up Your Data: Back up your QuickBooks data regularly. QuickBooks offers options for backing up your data to a local drive or to the cloud. In the event of data loss due to hardware failure, software corruption, or other unforeseen circumstances, having a recent backup ensures you can restore your financial information.
- Limit User Access: Control who has access to your QuickBooks file. Grant access only to trusted individuals and assign them the minimum necessary permissions. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.
- Be Wary of Phishing: Be cautious of phishing attempts. Phishing is a type of cyberattack where attackers try to trick you into revealing sensitive information, such as your password or credit card details. Do not click on suspicious links or open attachments from unknown senders. Always access QuickBooks directly through its official website or app.
- Monitor Account Activity: Regularly review your QuickBooks account activity for any suspicious transactions or unauthorized changes. If you notice anything unusual, immediately change your password and contact QuickBooks support.
- Secure Your Devices: Protect your devices (computer, smartphone, tablet) with strong passwords, up-to-date antivirus software, and firewalls. Ensure that your devices are protected from malware and other threats that could compromise your data.
Importance of Regularly Updating QuickBooks Software
Keeping your QuickBooks software up to date is crucial for maintaining security. Software updates often include critical security patches and enhancements that protect your data from the latest threats.
- Security Patches: Software updates frequently include security patches that address known vulnerabilities in the software. These patches fix security holes that could be exploited by hackers to gain access to your data. Ignoring updates leaves your data exposed to these risks.
- Bug Fixes: Updates also include bug fixes that can improve the stability and reliability of the software. Bugs can sometimes create security loopholes or lead to data corruption, so it is important to address them promptly.
- Performance Enhancements: Updates can improve the performance and efficiency of QuickBooks, making it easier to use and reducing the risk of errors.
- Compliance with Security Standards: Intuit regularly updates QuickBooks to comply with evolving security standards and regulations. Staying up to date ensures that your software meets the latest security requirements.
- Automatic Updates: QuickBooks typically offers automatic updates. Enable automatic updates to ensure that you are always running the latest version of the software and benefiting from the latest security features. If you have disabled automatic updates, check for updates regularly and install them promptly.