Understanding Crypto Wallet Types
How to create a crypto wallet – Crypto wallets are essential tools for storing and managing your digital assets. Understanding the different types available is crucial for selecting the most appropriate option based on your security needs and technical expertise. This section will explore the key differences between hot and cold wallets, their respective security implications, and provide examples of popular options.
Hot Wallets vs. Cold Wallets
The primary distinction lies in their connectivity to the internet. Hot wallets, always connected to the internet, offer convenience but sacrifice security. Cold wallets, offline storage devices, prioritize security over ease of access.
Security Implications of Hot and Cold Wallets
Hot wallets are vulnerable to hacking and malware due to their constant internet connection. Cold wallets, being offline, are significantly more secure against online threats. However, physical loss or damage to a cold wallet can lead to irreversible loss of funds.
Examples of Hot and Cold Wallets
Popular hot wallets include MetaMask (browser extension), Trust Wallet (mobile app), and Coinbase Wallet (mobile app). These offer user-friendly interfaces and seamless integration with decentralized applications (dApps). However, their security relies heavily on strong passwords and secure device practices. Examples of cold wallets include Ledger Nano S Plus and Trezor Model T. These hardware wallets provide enhanced security through offline storage and robust security features, but they require a higher level of technical understanding to set up and use.
Comparison of Wallet Types
| Type | Security | Accessibility | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware Wallet (e.g., Ledger, Trezor) | High (offline storage) | Moderate (requires device connection) | Medium to High |
| Software Wallet (e.g., MetaMask, Trust Wallet) | Medium (vulnerable to online threats) | High (accessible anytime, anywhere) | Low to Free |
| Paper Wallet | Medium (vulnerable to physical damage and loss) | Low (requires manual entry of keys) | Very Low (essentially free) |
Choosing the Right Wallet
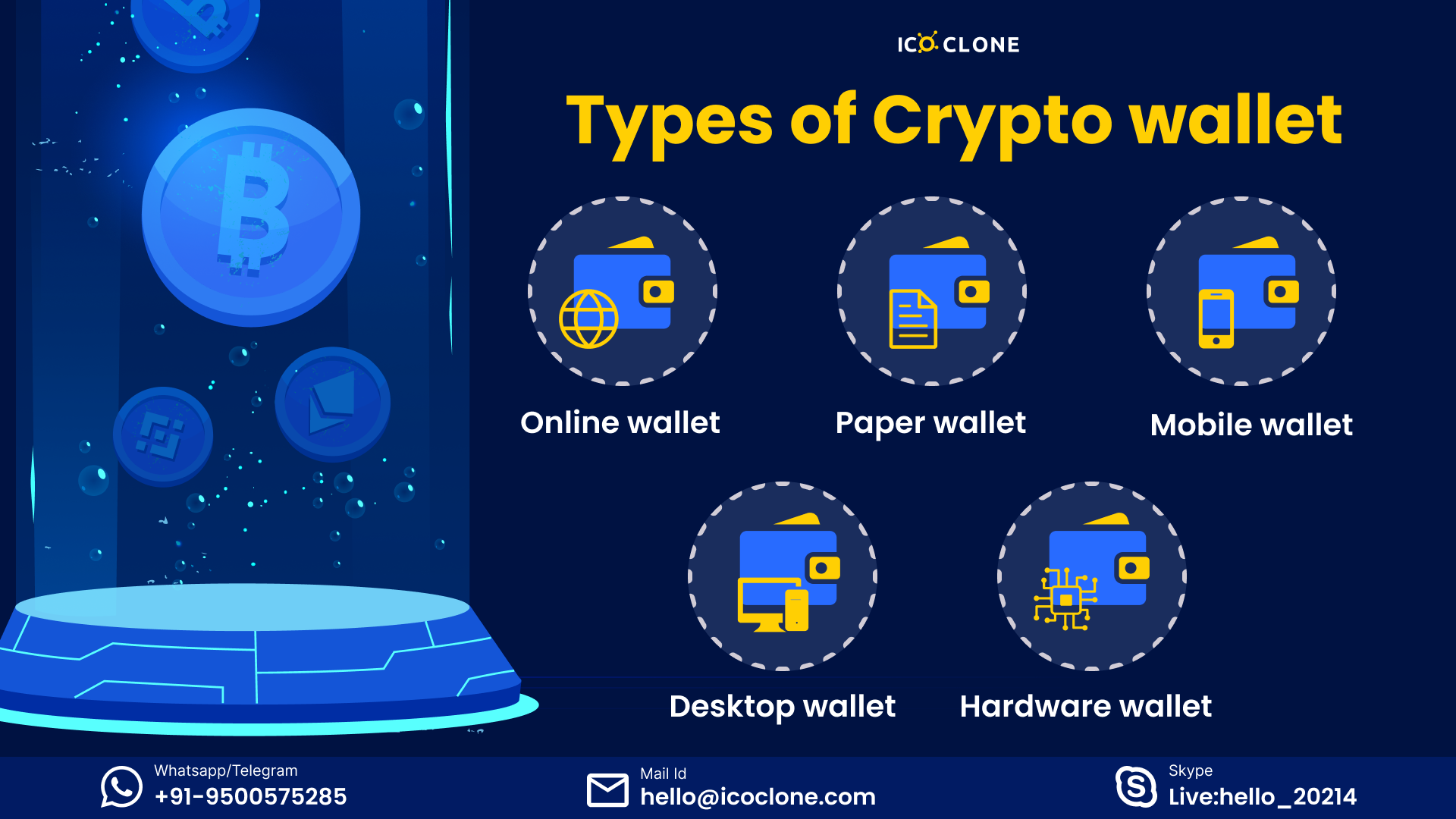
Selecting the appropriate crypto wallet requires careful consideration of several factors, balancing security and convenience based on individual needs and technical skills. This section will provide guidance on making an informed decision.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Crypto Wallet
- Supported Cryptocurrencies: Ensure the wallet supports the specific cryptocurrencies you intend to store.
- User-Friendliness: Choose a wallet with an intuitive interface, especially if you’re a beginner.
- Security Features: Prioritize wallets with robust security features like two-factor authentication (2FA) and strong encryption.
- Reputation and Security Practices: Research the wallet provider’s track record and security measures.
Security vs. Convenience Trade-offs
Hot wallets prioritize convenience but compromise security, while cold wallets offer superior security at the cost of reduced accessibility. The optimal choice depends on the amount and type of cryptocurrency being stored and the user’s risk tolerance.
Wallet Selection Based on User Experience and Technical Expertise
Beginners should opt for user-friendly software wallets or consider hardware wallets with good user support. Experienced users may prefer more advanced options offering greater control and customization.
Researching Wallet Providers’ Reputation and Security Practices
Thorough research is essential. Check for independent security audits, reviews, and community feedback before selecting a wallet provider.
Setting Up a Crypto Wallet (Software Wallet Example)
This section details the process of setting up a software wallet, using MetaMask as an example. Remember, always back up your seed phrase and follow best practices for security.
Step-by-Step Process of Creating a MetaMask Account
- Download the MetaMask browser extension or mobile app.
- Create a new wallet and securely store your seed phrase.
- Set a strong password and enable 2FA if available.
- Add your desired networks (e.g., Ethereum Mainnet).
Backing Up a Software Wallet’s Seed Phrase or Private Keys
Write down your seed phrase on paper and store it securely in a safe place, away from your computer and other digital devices. Never share your seed phrase with anyone.
Flowchart Illustrating Software Wallet Setup and Security

A flowchart would visually represent the steps: Downloading the wallet, creating an account, securing the seed phrase, setting a password, enabling 2FA, and regularly updating the software. It would show a clear path from initial setup to secure usage.
Best Practices for Securing a Software Wallet
- Use a strong, unique password.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA).
- Keep your software updated.
- Use a reputable antivirus program.
Setting Up a Crypto Wallet (Hardware Wallet Example)
This section Artikels the process of setting up a hardware wallet, using a Ledger Nano S Plus as an example. Hardware wallets provide a higher level of security compared to software wallets.
Setting Up a Hardware Wallet
- Connect the hardware wallet to your computer.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to create a new wallet and generate a seed phrase.
- Securely store your seed phrase offline.
- Set a PIN code for your hardware wallet.
Transferring Cryptocurrency to a Hardware Wallet
- Obtain the receiving address from your hardware wallet.
- Initiate a transaction from your existing wallet to the hardware wallet’s address.
- Confirm the transaction on your hardware wallet.
Potential Security Risks and Mitigation Strategies
- Physical loss or theft: Store the wallet securely and consider insurance.
- Phishing attacks: Be cautious of suspicious emails or websites.
- Firmware vulnerabilities: Keep the wallet’s firmware updated.
Importance of Physically Securing a Hardware Wallet
Keep your hardware wallet in a safe, secure location, away from potential threats. Consider using a safe or other secure storage solution.
Securing Your Crypto Wallet: How To Create A Crypto Wallet
Protecting your crypto wallet from unauthorized access is paramount. This section explores various security measures to safeguard your digital assets.
Methods for Protecting a Crypto Wallet
- Strong Passwords: Use long, complex, and unique passwords.
- Biometrics: Utilize biometric authentication if available.
- Multi-Signature Wallets: Require multiple signatures for transactions.
Comparison of Security Measures
Multi-signature wallets offer the highest security, followed by biometric authentication and strong passwords. The effectiveness of each method depends on its proper implementation.
Consequences of Losing Access to a Crypto Wallet
Losing access to your wallet can result in the permanent loss of your cryptocurrency. Without the seed phrase or private keys, recovery is generally impossible.
Best Practices for Maintaining Wallet Security, How to create a crypto wallet
- Use strong, unique passwords.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA).
- Regularly back up your seed phrase.
- Be cautious of phishing attempts.
- Keep your software and firmware updated.
Managing and Using Your Crypto Wallet
This section covers the practical aspects of managing and using your crypto wallet, including sending, receiving, and recovering funds.
Sending and Receiving Cryptocurrency
The process generally involves obtaining the recipient’s public address, entering the amount to send, and confirming the transaction. Receiving cryptocurrency involves providing your wallet’s public address to the sender.
Checking Balance and Transaction History
Most wallets provide a clear overview of your balance and a detailed transaction history, allowing you to track your cryptocurrency movements.
Recovering a Lost or Compromised Wallet
If you have a backup of your seed phrase, you can recover your wallet. If not, recovery is usually not possible.
Step-by-Step Guide on Using a Specific Crypto Wallet
A detailed guide, specific to a chosen wallet (e.g., MetaMask), would illustrate the process of sending, receiving, and potentially staking cryptocurrency within that platform. This would involve screenshots or detailed descriptions of each step.
Understanding Wallet Fees and Transaction Costs
Cryptocurrency transactions involve various fees. Understanding these costs is crucial for budgeting and managing your funds effectively.
Types of Wallet Fees
- Transaction Fees: Fees charged by the wallet provider for processing transactions.
- Network Fees (Gas Fees): Fees paid to miners or validators for confirming transactions on the blockchain.
Fee Calculation and Influencing Factors
Transaction fees vary depending on the wallet provider, while network fees are influenced by network congestion and transaction speed.
Comparison of Transaction Fees Across Different Cryptocurrencies and Wallets
Transaction fees differ significantly between cryptocurrencies (e.g., Bitcoin vs. Ethereum) and wallets. Some wallets may offer lower fees than others.
Table Outlining Typical Fees
| Wallet/Cryptocurrency | Transaction Type | Typical Fee | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| MetaMask (Ethereum) | Send ETH | Variable (depends on network congestion) | Can range from a few cents to several dollars. |
| Coinbase (Bitcoin) | Send BTC | Variable (depends on network fees) | Typically higher than Ethereum transactions. |
| Ledger Live (Various) | Send various crypto | Variable (depends on network and cryptocurrency) | Fees vary depending on the chosen cryptocurrency. |