Defining Non-Employee Travel Reimbursement
Non-employee travel reimbursement is a crucial aspect of managing business expenses for independent contractors, freelancers, and other non-employee personnel. It differs significantly from employee travel reimbursement, requiring careful attention to both the financial and legal implications. Understanding these differences is essential for both the payer and the recipient to ensure compliance and avoid potential tax issues.
Non-employee travel reimbursement policies Artikel how expenses incurred during business-related travel are handled. This includes defining the scope of eligible expenses, the documentation requirements, and the payment procedures. Key differences lie in the tax treatment, liability, and the overall contractual agreement between the parties involved.
Non-Employee Travel Reimbursement Defined
Non-employee travel reimbursement refers to the payment of expenses incurred by a non-employee while traveling for business purposes. This payment is made by a company or organization to an independent contractor or other non-employee. The reimbursements typically cover costs associated with travel, accommodation, meals, and transportation, all directly related to the work performed.
Differences Between Employee and Non-Employee Travel Reimbursement Policies
Employee travel reimbursement is often part of an employee’s compensation package, whereas non-employee reimbursement is a separate contractual agreement. Employee reimbursements are usually handled through company policies and procedures, while non-employee reimbursements are governed by the terms of a contract or agreement. Employee reimbursements are generally tax-advantaged, while non-employee reimbursements are treated as income subject to self-employment taxes and potentially other applicable taxes. This crucial distinction highlights the importance of carefully defining the reimbursement structure in non-employee contracts.
Legal and Tax Implications
Properly documenting and managing non-employee travel reimbursements is essential to comply with tax laws and avoid potential penalties. Failure to adhere to the rules could result in tax audits and significant financial consequences. The payer must ensure that the reimbursements are reasonable and directly related to the work performed. The recipient must accurately report the reimbursement as income on their tax returns. A key element is to maintain meticulous records of all expenses.
Types of Non-Employee Travel Reimbursement
Various expenses can be reimbursed, depending on the nature of the work and the agreement. Common types include:
- Mileage: Reimbursement for the use of a personal vehicle for travel. This is often calculated based on IRS mileage rates.
- Lodging: Reimbursement for accommodations, such as hotels or rentals, incurred during business travel.
- Meals: Reimbursement for meals consumed during business travel. These are typically subject to specific guidelines regarding receipts and documentation.
- Transportation: Reimbursement for airfare, train tickets, or other transportation costs incurred for business travel.
Comparison of Employee and Non-Employee Reimbursement Policies
The following table highlights the key differences between employee and non-employee travel reimbursement policies:
| Policy Type | Eligibility | Expense Types | Documentation Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Employee | Employees of the company | Company-approved expenses | Expense reports, receipts, and possibly approval forms |
| Non-Employee | Independent contractors, freelancers, or other non-employees | Expenses directly related to the contracted work | Detailed receipts, expense reports, and potentially invoices or contracts |
1099 Independent Contractor Travel Reimbursement
Navigating travel reimbursements for independent contractors (1099 workers) requires a meticulous approach. Proper documentation and adherence to IRS guidelines are crucial to avoid potential tax issues for both the contractor and the company. This section dives into the specific considerations, tax implications, and best practices for managing these reimbursements effectively.
Understanding the unique tax implications for 1099 contractors is paramount. Unlike employees, 1099 workers are responsible for paying their own taxes, including self-employment tax. This means that reimbursements for travel expenses are treated differently than for employees. The company’s payment of reimbursement acts as income for the contractor, but the method of payment and documentation will directly affect the contractor’s and company’s tax burden.
Specific Considerations for 1099 Contractors
1099 contractors have significant autonomy in managing their travel expenses. This autonomy necessitates careful tracking and documentation to ensure compliance. Contractors should maintain detailed records of all travel expenses, including receipts, mileage logs, and itinerary details. This allows for accurate reporting and reconciliation of expenses. The company should also be meticulous in verifying the validity and reasonableness of these expenses.
Tax Implications for Contractor and Company
The tax implications for both the contractor and the company differ significantly from employee travel reimbursements. For the contractor, the reimbursement is considered income, and they are responsible for paying self-employment taxes (Social Security and Medicare) on the amount. The company must report the payment as a business expense. Accurate record-keeping is crucial to ensure both parties adhere to tax regulations. The IRS closely monitors 1099 contractor reimbursements, and discrepancies can lead to audits.
Methods for Tracking and Documenting Travel Expenses
Maintaining meticulous records is key for both the contractor and the company. This includes detailed receipts for all expenses, including transportation, lodging, meals, and incidentals. A clear and concise travel itinerary helps track the business purpose of each trip. A mileage log is essential if the contractor uses their personal vehicle. The contractor should clearly Artikel the business purpose of the trip and the specific tasks completed.
- Receipts: All receipts should be kept in a secure and organized manner, including those for lodging, meals, transportation, and any other expenses.
- Mileage Logs: For travel by personal vehicle, detailed mileage logs are essential, noting the start and end points, dates, and purposes of each trip.
- Itinerary: A detailed itinerary outlining the dates, locations, and activities of the trip provides a comprehensive record.
- Expense Reports: Regular expense reports should be submitted to the company, following a standardized format. This includes a detailed description of the expenses and the rationale behind each expense.
Different Reimbursement Methodologies
Different reimbursement methods exist for 1099 contractors, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Companies can choose from advance payments, reimbursement on submission of receipts, or a combination of both.
- Advance Payments: Advance payments can streamline the process, allowing contractors to cover expenses upfront. However, it’s essential to establish clear guidelines and procedures for reimbursements to avoid issues.
- Reimbursement on Submission of Receipts: This method requires contractors to submit receipts for reimbursement. This method promotes accuracy and accountability, as receipts provide concrete proof of expenses.
- Combination Method: Combining advance payments with reimbursement on receipt submission can balance efficiency and accountability. This method provides some flexibility while maintaining a strong record of expenses.
Sample Reimbursement Policy for 1099 Contractors
This policy Artikels the procedures for reimbursement of travel expenses for 1099 contractors.
Company Name 1099 Contractor Travel Reimbursement Policy
- Purpose: This policy Artikels the procedures for reimbursement of travel expenses incurred by 1099 contractors while performing work for [Company Name].
- Eligibility: All 1099 contractors performing work for [Company Name] are eligible for reimbursement.
- Expense Types: Reimbursable expenses include transportation, lodging, meals, and incidentals directly related to the performance of work.
- Documentation Requirements: All reimbursements must be supported by original receipts, including dates, locations, amounts, and a clear description of the expense.
- Reimbursement Process: Contractors must submit a detailed expense report within [number] days of the trip. Reports must be submitted through [specified method].
- Review and Approval: The company will review the submitted reports for accuracy and compliance with this policy. Reimbursements will be processed within [number] business days.
- Receipt Retention: Original receipts must be retained by the contractor for [number] years for tax and audit purposes.
Documentation and Record-Keeping: Non Employee Travel Reimbursement 1099

Accurate documentation is crucial for smooth and compliant non-employee travel reimbursements. Thorough record-keeping ensures that reimbursements are processed fairly and efficiently, avoiding potential disputes or audits. This meticulous approach protects both the independent contractor and the company, promoting transparency and trust in the process.
Importance of Accurate Documentation
Precise documentation is paramount for several reasons. It serves as a verifiable record of expenses incurred during travel, enabling the quick and accurate processing of reimbursements. Proper documentation minimizes potential disputes or misunderstandings, especially if there’s a discrepancy between the claimed expenses and the actual expenses incurred. It also helps in complying with tax regulations and internal policies, avoiding penalties and ensuring a smooth reimbursement process for all parties involved.
Examples of Required Documentation
A comprehensive documentation package typically includes several key elements. These records offer a detailed picture of the travel activity, justifying the claimed expenses. Receipts, travel itineraries, and expense reports are fundamental components of this documentation package. Receipts provide evidence of the expenses incurred, while itineraries detail the travel dates, locations, and purpose. Expense reports consolidate the information from receipts and itineraries into a structured format for reimbursement processing.
Procedures for Maintaining Records
Maintaining organized records is essential to a smooth reimbursement process. This includes creating a dedicated file or folder for each travel reimbursement claim. Each receipt should be meticulously stored in this file, with a clear description of the expense. Ensure proper labeling and sequential numbering for easy retrieval and reference. This structured approach allows for quick access to documents when needed, facilitating the timely processing of reimbursements. Regular reviews and updates to these records are also recommended to ensure accuracy and completeness.
Types of Receipts Required
Maintaining detailed records requires a clear understanding of the types of receipts needed for different expenses. This allows for a consistent and organized record-keeping system. A comprehensive approach includes collecting receipts for all necessary expenses, ensuring proper classification and storage. The following table Artikels the necessary receipts for various expenses:
| Expense Type | Required Receipts | Acceptable Formats |
|---|---|---|
| Accommodation | Hotel bills, Airbnb confirmations, or other lodging receipts | Printed copies, scanned copies, or digital confirmations |
| Transportation | Airline tickets, train tickets, or taxi receipts | Printed copies, scanned copies, or digital copies |
| Meals | Restaurant receipts, or meal vouchers | Printed copies, scanned copies, or photos of receipts |
| Parking | Parking tickets or receipts | Printed copies, scanned copies, or digital confirmations |
| Other | Specific receipts for each expense, like rental car agreements | Printed copies, scanned copies, or digital confirmations. |
Compliance and Reporting Requirements

Navigating the complexities of 1099 travel reimbursements requires meticulous attention to IRS guidelines. Understanding the specific rules for both the payer and the recipient is crucial to avoid potential tax issues and penalties. This section Artikels the necessary steps for compliance and reporting.
IRS Guidelines for Non-Employee Travel Reimbursements
The IRS mandates specific rules for reimbursing independent contractors for business travel expenses. These guidelines ensure accurate reporting and taxation of such reimbursements. The IRS considers travel expenses as deductible business expenses for both the payer and the recipient, subject to specific limits and documentation requirements. Proper classification and documentation are essential for compliance.
Reporting Requirements for Payers
Accurate record-keeping is paramount for the payer. They must maintain detailed records of the reimbursement, including the amount, date, and purpose of the travel. This documentation is essential for tax purposes and to demonstrate compliance.
- Detailed Expense Reports: The payer must maintain a comprehensive record of all travel expenses, including receipts, invoices, and travel itineraries. This comprehensive documentation is essential for verification and ensures compliance.
- Proper Classification: The payer must correctly classify the reimbursed expenses as business expenses, and clearly indicate the nature of the services performed by the independent contractor. This will be necessary for accurate reporting to the IRS.
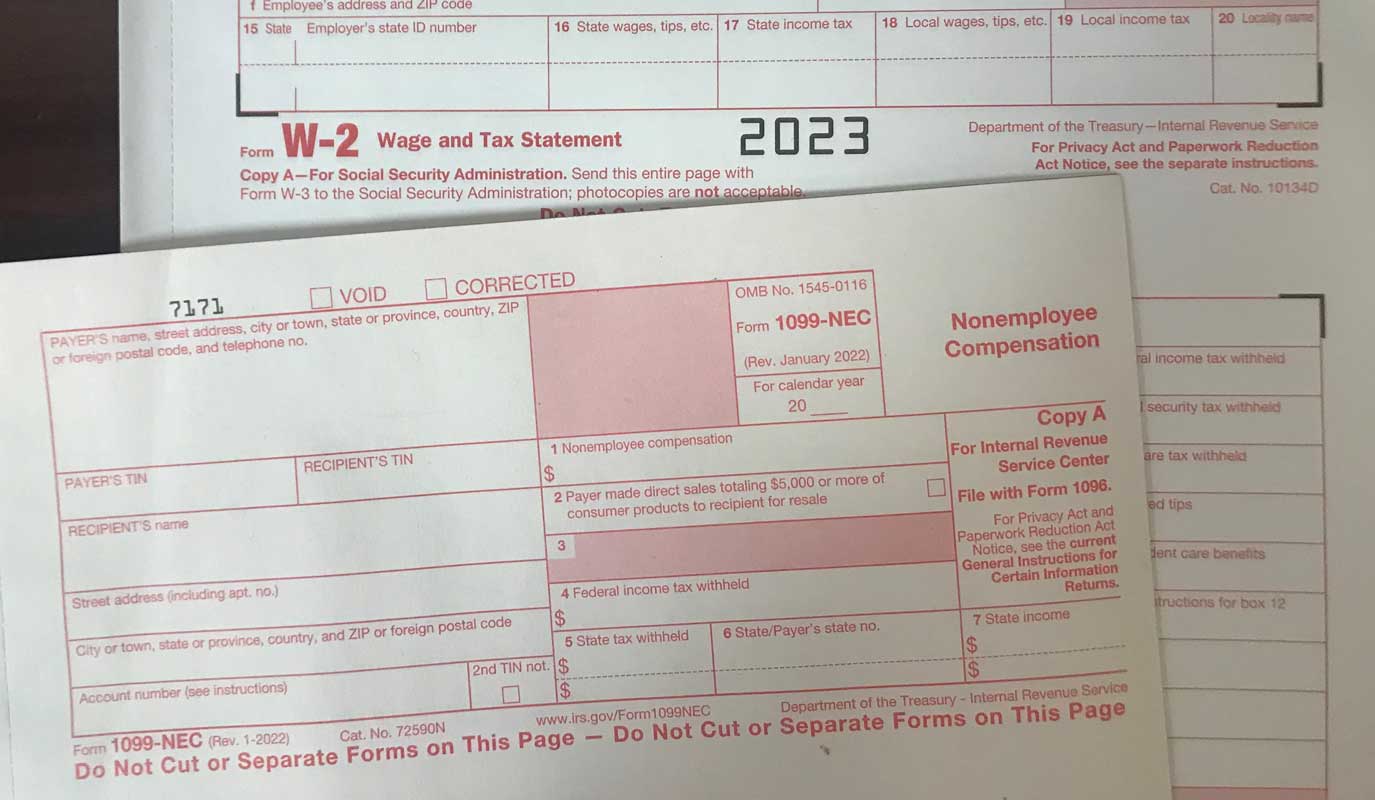
- Form 1099-NEC: The payer must issue Form 1099-NEC to the independent contractor by January 31st of the following year, reporting the total amount paid in the prior tax year. Failure to do so can lead to penalties.
Reporting Requirements for Recipients
Recipients (independent contractors) also have specific reporting obligations. They are responsible for accurately reporting the reimbursements as income on their tax returns.
- Accurate Reporting on Tax Returns: The independent contractor must report the reimbursement as income on Schedule C (Profit or Loss from Business) or as other income on their tax return. This is a crucial step in ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
- Maintaining Records: Recipients should maintain copies of all receipts, invoices, and other documentation related to the reimbursed expenses. This allows for verification and accurate reporting.
Potential Tax Issues
Improper reimbursement practices can lead to various tax issues. Failure to comply with IRS guidelines may result in penalties, audits, and legal ramifications. Examples of improper practices include inaccurate reporting, misclassification of expenses, and failure to issue proper documentation.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Non-compliance with IRS guidelines can lead to significant penalties. These penalties can vary depending on the severity of the violation and may include monetary fines and interest charges. The IRS takes non-compliance very seriously, and penalties can be substantial.
Step-by-Step Guide to Compliance
A structured approach to compliance minimizes the risk of errors and penalties.
- Classify the Relationship: Ensure the relationship is properly classified as a 1099 independent contractor, not an employee. This is crucial for compliance with IRS regulations.
- Document All Expenses: Maintain meticulous records of all expenses, including receipts, invoices, and itineraries. Proper documentation is vital for accuracy.
- Issue 1099-NEC Forms: Issue Form 1099-NEC to the independent contractor by January 31st of the following tax year. This form reports the total payments made to the contractor during the prior tax year.
- Accurately Report Income: The independent contractor must report the reimbursement as income on their tax return (Schedule C, or other appropriate income section). Accuracy is paramount for compliance.
- Consult a Tax Professional (if needed): Seeking professional guidance from a tax advisor can help clarify any ambiguities and ensure compliance with the most up-to-date IRS regulations. This can be especially beneficial for complex situations.
Methods for Managing Reimbursements
Streamlining non-employee travel reimbursements is crucial for maintaining accurate records and avoiding potential disputes. A well-defined system ensures transparency, facilitates timely payments, and simplifies the entire process for both the company and the independent contractor. This section details effective methods for managing these reimbursements.
Effective reimbursement management requires a structured approach, from initial expense tracking to final payment. A robust system minimizes errors, builds trust, and helps both parties maintain accurate financial records.
Expense Reporting Methods
A clear and concise expense reporting method is essential for accurate tracking. This can range from simple paper forms to sophisticated online platforms. Paper forms, while straightforward in some cases, often require manual data entry and can be prone to errors.
- Traditional Expense Reports: Paper-based expense reports, while familiar, often involve manual data entry and are more susceptible to errors, especially if not meticulously maintained. Maintaining organized and detailed records is paramount. Detailed receipts are crucial for validating expenses and reducing disputes.
- Online Expense Reporting Platforms: Modern platforms streamline the process by allowing contractors to submit expense reports digitally, often with automatic receipt attachments. These platforms facilitate real-time expense tracking, automatic calculations, and simplified approval workflows. This approach typically reduces errors and improves efficiency.
Software Solutions for Expense Tracking
Choosing the right software is crucial for managing non-employee travel reimbursements efficiently. Several solutions are available, catering to varying needs and budgets. Some popular software options offer robust features like automatic expense categorization, receipt management, and automated approval workflows.
- Expensify: A popular choice, Expensify allows users to capture expenses via mobile app, email, and web, and it automatically categorizes expenses and attaches receipts. This simplifies the process and ensures accurate reporting.
- Concur: Concur is another widely used platform that offers comprehensive expense management features, including robust reporting capabilities, detailed expense analysis, and streamlined approval processes. This comprehensive software is particularly beneficial for larger companies with numerous travel reimbursements.
- Zoho Expense: Zoho Expense is a cloud-based expense management solution that helps manage and track travel expenses for businesses and independent contractors. This software provides automated expense reports, receipt management, and reporting tools.
Importance of Timely Reimbursements
Prompt reimbursements are vital for maintaining a positive relationship with independent contractors. Delays can create frustration and financial hardship. A well-defined timeline for processing and approving reimbursements minimizes delays and fosters trust.
A clear and transparent reimbursement policy fosters a positive relationship between the company and the independent contractor.
Best Practices for Avoiding Disputes and Errors
Implementing clear policies and procedures minimizes errors and disputes. This includes specific guidelines for expense documentation, receipt requirements, and the reimbursement process itself. Thorough documentation is crucial.
- Clear Policy Documentation: A detailed policy outlining the reimbursement process, including acceptable expenses, receipt requirements, and the timeframe for reimbursement, reduces ambiguity and minimizes disputes. This document should be easily accessible to all parties.
- Detailed Receipt Requirements: Establishing specific receipt requirements (e.g., date, vendor, description) prevents disputes and ensures proper validation of expenses. The policy should specify the acceptable forms of receipts.
- Internal Controls: Establishing clear approval procedures, roles, and responsibilities for each step of the reimbursement process prevents errors and ensures accountability. This includes a designated individual or team responsible for approving expenses.
Reimbursement Process Flowchart
A flowchart visually represents the reimbursement process, making it easy to understand and follow. This helps ensure that all steps are completed accurately and in a timely manner.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Contractor submits expense report with receipts. |
| 2 | Finance department reviews the report and receipts. |
| 3 | Finance department approves or rejects the report. |
| 4 | If approved, payment is processed. |
| 5 | Contractor receives reimbursement. |
Avoiding Common Mistakes
Navigating the intricacies of non-employee travel reimbursements for 1099 independent contractors can be tricky. Mistakes, though often unintentional, can lead to significant problems, ranging from tax penalties to legal disputes. Understanding potential pitfalls and implementing preventive measures is crucial for smooth operations and compliance.
Careful attention to detail and adherence to established procedures are paramount in avoiding these errors. A robust system for documenting and verifying expenses, combined with a clear understanding of the rules and regulations, is essential to maintain compliance and protect your business.
Common Mistakes in Reimbursement Processes
Several errors frequently arise in non-employee travel reimbursement processes. These include incorrect documentation, missing or incomplete forms, and failure to adhere to company policies. Understanding these errors is vital for proactive prevention.
- Inaccurate Expense Reporting: Misrepresenting travel expenses, such as claiming meals or lodging not actually incurred, is a significant error. This can result in significant penalties and legal action, potentially jeopardizing the business relationship between the contractor and the client.
- Insufficient Documentation: Lack of proper receipts, itineraries, or other supporting documents can lead to reimbursement disputes. Clear documentation is crucial to substantiate the claimed expenses.
- Failure to Comply with Policy: Ignoring company-specific travel reimbursement policies can lead to disputes and rejection of claims. Understanding and adhering to the stipulated policies is critical for a smooth reimbursement process.
- Timing Issues: Submitting reimbursement claims after the established deadline or without proper supporting documents can result in delays or rejection. Adhering to the set timelines is essential.
Potential Consequences of Mistakes
The consequences of errors in non-employee travel reimbursement processes can range from minor inconveniences to substantial penalties and legal issues. These consequences should not be underestimated.
- Tax Penalties: Incorrect reporting of income or expenses can trigger IRS audits and substantial tax penalties. These penalties can be costly and time-consuming to resolve.
- Legal Disputes: Failure to comply with legal requirements or company policies can lead to legal disputes. These disputes can strain business relationships and result in financial losses.
- Damage to Reputation: Repeated errors or non-compliance can tarnish the reputation of both the contractor and the client. This can negatively impact future business opportunities.
- Delayed Payments: Incomplete or inaccurate documentation can lead to delays in reimbursement payments. This can disrupt the contractor’s financial planning and workflow.
Solutions to Avoid Errors
Implementing preventative measures can significantly reduce the risk of errors in non-employee travel reimbursement processes. Proactive steps are essential for maintaining compliance.
- Clear Policy Implementation: Establish a comprehensive and easily accessible policy for travel reimbursements, outlining requirements for documentation, deadlines, and claim procedures. This should be communicated clearly to both the employer and the independent contractor.
- Thorough Documentation: Ensure all expenses are meticulously documented with receipts, itineraries, and other supporting evidence. Keep digital copies of these documents for easy access and verification.
- Regular Training: Provide training sessions to all involved parties to reinforce understanding of the reimbursement policy and procedures. This ensures everyone is well-versed in the requirements.
- Establish a Review Process: Implement a robust review process for all reimbursements to verify accuracy and compliance with company policies. This ensures that claims are handled promptly and correctly.
Checklist for Verifying Reimbursements
This checklist provides a systematic approach to verifying the accuracy of reimbursements. Regular use of this checklist is highly recommended.
| Item | Verification |
|---|---|
| Receipt | Verify authenticity and accuracy of amounts. |
| Itinerary | Confirm dates and locations of travel. |
| Expense Details | Ensure claimed expenses align with the policy. |
| Policy Adherence | Check compliance with company travel policies. |
| Submission Deadline | Confirm submission within the stipulated timeframe. |
Illustrative Scenarios
Navigating non-employee travel reimbursements for 1099 contractors requires a nuanced approach. Different situations demand tailored handling, from simple overnight trips to complex international excursions. This section provides illustrative scenarios to help you understand the best practices for handling various reimbursement requests.
International Travel Reimbursements
International travel presents unique challenges due to fluctuating currency exchange rates, differing tax regulations, and potential visa requirements. Thorough pre-trip planning is crucial. Establish clear guidelines for currency exchange, including the preferred exchange method and associated fees. Ensure that the contractor understands and complies with all applicable tax regulations in both the originating and destination countries.
Overnight Stays
When an independent contractor requires an overnight stay, the reimbursement process needs to address lodging costs. A detailed description of the lodging arrangements, including the name of the hotel, dates of stay, and room type, is essential. Always ensure that the lodging aligns with the project’s scope of work and is a reasonable business expense. Specify the policy regarding meal allowances or reimbursements.
Unusual or Complex Expenses, Non employee travel reimbursement 1099
Unforeseen circumstances can lead to unusual or complex expenses. These could include unexpected medical expenses, security fees, or emergency evacuation costs. Establish a clear process for handling such expenses. For instance, request detailed receipts, supporting documentation, and a clear explanation of the necessity of the expense. Consult with legal counsel to understand potential tax implications of these types of expenses.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Reimbursement policies should remain adaptable to address unique situations. Unexpected events, such as weather delays or flight cancellations, can impact travel plans. Be prepared to offer flexible reimbursement options in response to these situations. For instance, if a flight is canceled, allow the contractor to provide evidence of a reasonable alternative and process the reimbursement accordingly. This flexibility avoids unnecessary delays and maintains a positive relationship.
Handling Multiple Expenses
A contractor might incur various expenses during a trip, including transportation, lodging, meals, and miscellaneous items. To effectively manage these, maintain a comprehensive expense report format. This format should include detailed descriptions of each expense, supporting documentation (receipts, invoices), and a total calculation of the expenses. It is essential to clearly define the policy for multiple expenses and categorize them appropriately. An organized and structured approach helps ensure accuracy and compliance.
Example of a Comprehensive Reimbursement Policy
| Expense Category | Reimbursement Policy |
|---|---|
| Transportation | Mileage rate or documented receipts for public transport |
| Lodging | Reasonable hotel rates, receipts required, and adherence to policy limits. |
| Meals | Per diem rates or receipts for meals exceeding per diem. |
| Miscellaneous Expenses | Receipts for all miscellaneous expenses and justification for the expenditure. |
A well-defined and transparent reimbursement policy is key to maintaining compliance and fostering trust with your independent contractors.
Non employee travel reimbursement 1099 – Navigating non-employee travel reimbursement, especially for 1099 contractors, can be tricky. Finding reliable travel arrangements is crucial, and a reputable travel agent like pinsight travel agent can simplify the process significantly. They can handle all the details, from booking flights and hotels to managing expense reports, ensuring a smooth and stress-free experience, making the entire 1099 travel reimbursement process much easier to manage.
Navigating non-employee travel reimbursement for 1099 contractors can be tricky. Understanding the nuances of these reimbursements is crucial for both the contractor and the client. A key aspect of successful reimbursement management is a clear understanding of the guidelines and procedures. To ensure your travel expenses are accurately documented and processed, consider seeking professional guidance from a travel SEO consultant, like the experts at travel seo consultant.
Ultimately, this meticulous approach to reimbursement management can save headaches and time, ensuring a smooth and profitable journey for everyone involved in the process.