The Significance of the Winter Solstice: Saturday Is The Winter Solstice And 2024’s Shortest Day. Here’s What

The winter solstice, occurring annually around December 21st or 22nd in the Northern Hemisphere and June 20th or 21st in the Southern Hemisphere, marks the shortest day and longest night of the year. This astronomical event holds profound significance across cultures and throughout history, influencing celebrations, traditions, and even our understanding of the cosmos.
The astronomical reason behind the winter solstice is the tilt of the Earth’s axis. Our planet is tilted at approximately 23.5 degrees relative to its orbital plane around the sun. This tilt means that during different parts of the year, different hemispheres receive more direct sunlight. During the winter solstice in the Northern Hemisphere, the Northern Hemisphere is tilted furthest away from the sun, resulting in the shortest day and longest night. Conversely, the Southern Hemisphere experiences its summer solstice, with the longest day and shortest night.
Historical and Cultural Significance of the Winter Solstice, Saturday is the winter solstice and 2024’s shortest day. Here’s what
The winter solstice has been observed and celebrated by various cultures for millennia. Many ancient societies viewed the solstice as a time of rebirth, renewal, and the return of the sun’s strength. The positioning of megalithic structures like Stonehenge in England suggests a sophisticated understanding of astronomy and the solstice’s significance to these ancient civilizations. These structures were often aligned to mark the solstices and equinoxes, demonstrating the importance of these astronomical events in their cultural practices. For example, the alignment of Stonehenge with the winter solstice sunrise provided a precise marker for the beginning of the winter season and its associated rituals.
Winter Solstice Celebrations and Traditions Worldwide
Celebrations and traditions surrounding the winter solstice vary considerably across the globe. In many cultures, the solstice is associated with festivals of light, symbolizing the triumph of light over darkness and the promise of returning sunlight.
Yule, a winter solstice festival celebrated by some Germanic and Norse peoples, involved feasting, bonfires, and the burning of Yule logs to symbolize the sun’s return. In ancient Rome, Saturnalia, a week-long festival honoring the god Saturn, was celebrated around the winter solstice. This period was characterized by revelry, gift-giving, and a temporary reversal of social norms. Modern celebrations often incorporate elements of these ancient traditions, such as decorating homes with lights and evergreen trees, exchanging gifts, and enjoying festive meals. In some parts of the world, the solstice is marked by gatherings, ceremonies, and rituals designed to honor the sun and welcome the lengthening days.
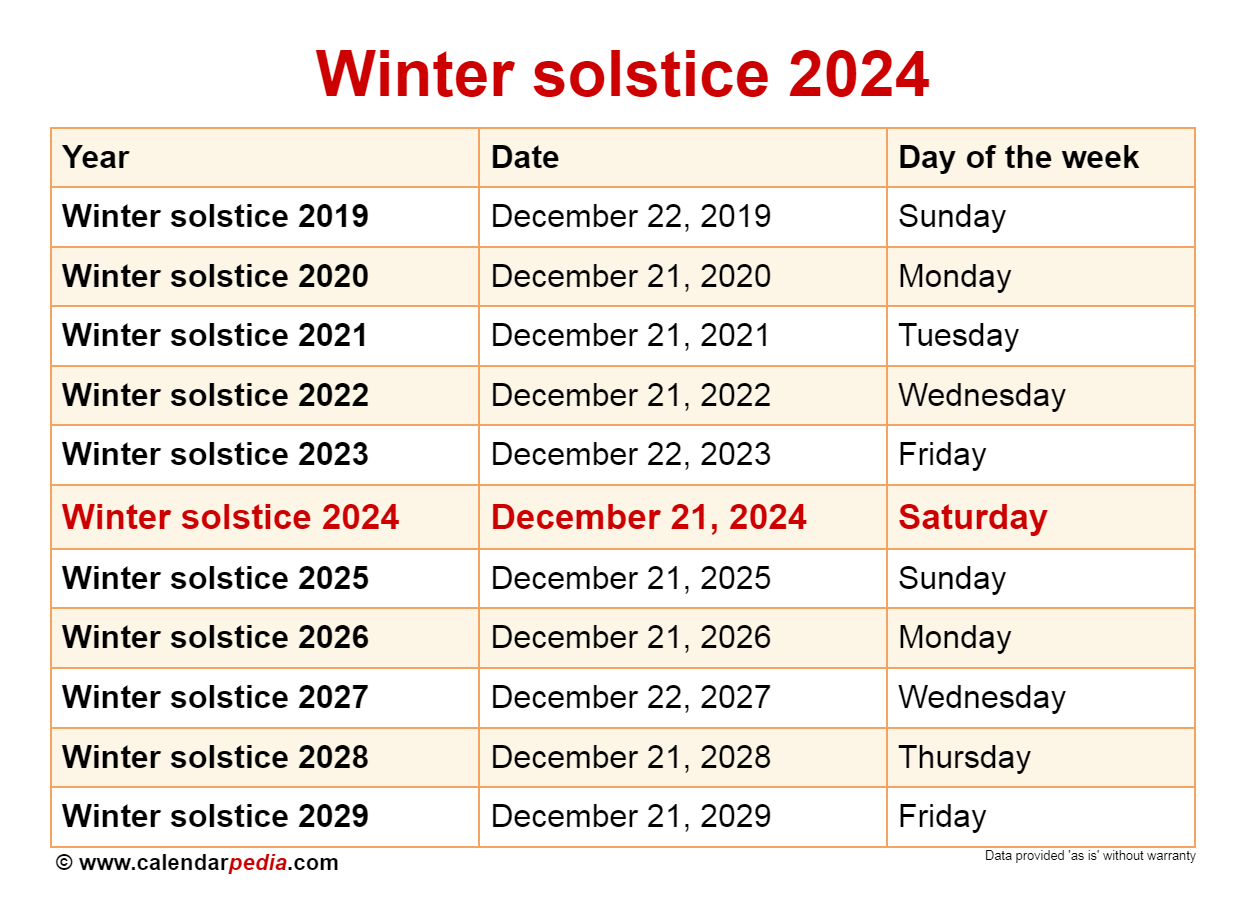
Winter Solstice Dates and Times in 2024
The following table provides the approximate dates and times for the winter solstice in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres for 2024. Note that the exact time varies slightly based on location.
| Hemisphere | Date (Approximate) | Time (Approximate UTC) | Time (Approximate your local time – adjust accordingly) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Northern | December 21, 2024 | 04:00 | [Insert your local time here] |
| Southern | June 20, 2024 | 10:58 | [Insert your local time here] |
Impact of the Winter Solstice on Modern Life
The winter solstice, while holding deep historical and cultural significance, also subtly influences various aspects of modern life. From everyday routines to large-scale economic activities, the shortest day of the year leaves its mark, prompting adjustments and adaptations across society.
Saturday is the winter solstice and 2024’s shortest day. Here’s what – The reduced daylight hours and colder temperatures associated with the winter solstice directly impact human behavior and societal structures. These impacts are not always dramatic, but they are pervasive and measurable in various ways.
Changes in Daily Activities and Lifestyles
The shorter days of the winter solstice often lead to alterations in daily routines. People tend to spend more time indoors, leading to increased energy consumption for heating and lighting. This shift in activity also affects social interactions, with outdoor activities often reduced and social gatherings possibly shifting to indoor venues. Furthermore, the decreased sunlight can affect mood and energy levels for some individuals, potentially leading to a greater reliance on artificial light sources and increased energy consumption.
Adaptation Strategies to Shorter Days and Colder Weather
Humans have developed numerous strategies to cope with the challenges presented by the winter solstice. These include technological adaptations, such as improved heating systems and energy-efficient lighting, as well as behavioral changes, such as adjusting work schedules to maximize daylight hours and engaging in indoor activities. Increased reliance on artificial light sources, including both indoor lighting and streetlights, also becomes evident during this period. The widespread adoption of central heating in many parts of the world directly mitigates the impact of the cold, enabling continued activity and comfort.
Economic Impacts of the Winter Solstice
The winter solstice has noticeable economic consequences. The tourism industry, for example, experiences a seasonal shift. Destinations known for winter sports see increased activity and revenue, while areas relying on outdoor tourism may experience a downturn. Conversely, the demand for energy increases significantly, particularly for heating, leading to higher energy bills for consumers and increased profits for energy providers. Retail sectors also adapt, with a focus on winter-related products and seasonal sales events. The increased demand for heating fuels and electricity leads to fluctuations in energy markets and prices.
Sector-Specific Impacts of the Winter Solstice
| Sector | Positive Impacts | Negative Impacts | Adaptations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tourism | Increased revenue in winter sports destinations | Decreased revenue in areas reliant on outdoor activities | Shifting marketing strategies, offering winter-themed packages |
| Energy | Increased demand and revenue for energy providers | Higher energy bills for consumers | Investing in energy-efficient technologies, implementing demand-side management strategies |
| Retail | Increased sales of winter-related products | Potential slowdown in sales of other goods | Seasonal promotions, marketing campaigns focused on winter products |
| Agriculture | Reduced crop production in some regions | Increased costs for maintaining livestock during harsh weather | Utilizing greenhouses, implementing protective measures for crops and livestock |