Defining a Specialty Finance Company
Specialty finance companies play a crucial role in the financial ecosystem, offering tailored financial solutions that often address the unmet needs of specific markets. They provide financing options that traditional banks may deem too risky or complex, filling a vital gap in the availability of capital. These companies are characterized by their focus and expertise in particular niches, allowing them to understand and serve their target customers more effectively.
Core Functions of a Specialty Finance Company
Specialty finance companies primarily provide financing, often in the form of loans or leases, to businesses and individuals. They evaluate creditworthiness, structure transactions, and manage the associated risks. They may also offer related services such as financial consulting or asset management. Their core function revolves around providing capital where traditional lenders may not.
Key Characteristics Distinguishing Specialty Finance Companies from Traditional Banks
Several characteristics differentiate specialty finance companies from traditional banks. These differences stem from their focus, risk appetite, and operational models.
- Target Market Focus: Specialty finance companies concentrate on specific industries, asset classes, or customer segments, allowing them to develop deep expertise and a competitive advantage. For example, a company might specialize in financing equipment for the construction industry or providing loans to small businesses.
- Risk Tolerance: They often have a higher risk tolerance than traditional banks, as they are willing to finance transactions that banks consider too risky. This can include loans to businesses with less established credit histories or financing for specialized assets.
- Operational Flexibility: Specialty finance companies often have more flexible and agile operational models, enabling them to adapt quickly to market changes and customer needs. This flexibility allows them to provide customized financing solutions.
- Funding Sources: They utilize a broader range of funding sources than traditional banks, including institutional investors, private equity firms, and securitization. This diversified funding model provides greater access to capital.
- Pricing: Due to the higher risk they take, specialty finance companies typically charge higher interest rates and fees compared to traditional banks. This pricing structure reflects the increased risk and specialized expertise they provide.
Primary Sectors Served by Specialty Finance Companies
Specialty finance companies serve a wide array of sectors, catering to the diverse needs of businesses and individuals. Their focus allows them to develop specialized expertise and offer tailored financial solutions.
- Equipment Finance: Financing the acquisition of various types of equipment, such as construction machinery, medical devices, and manufacturing equipment. For instance, a specialty finance company might provide a lease for a new MRI machine to a hospital.
- Commercial Real Estate Finance: Providing financing for commercial properties, including office buildings, retail spaces, and industrial facilities. This can involve bridge loans, construction loans, or permanent financing.
- Factoring and Accounts Receivable Financing: Offering short-term financing based on a company’s outstanding invoices or accounts receivable. This helps businesses improve cash flow.
- Consumer Finance: Providing loans to consumers for various purposes, such as home improvements, debt consolidation, or purchasing vehicles. This sector can include subprime lending.
- Healthcare Finance: Financing for healthcare providers, including hospitals, clinics, and physician practices. This can involve equipment financing, working capital loans, and revenue cycle management solutions.
- Transportation Finance: Financing for the acquisition of vehicles and equipment used in transportation, such as trucks, trailers, and aircraft.
- Film and Entertainment Finance: Providing financing for film production, television shows, and other entertainment projects. This includes production loans and distribution financing.
- Franchise Finance: Offering loans and financing solutions to franchisees.
Types of Specialty Finance Companies
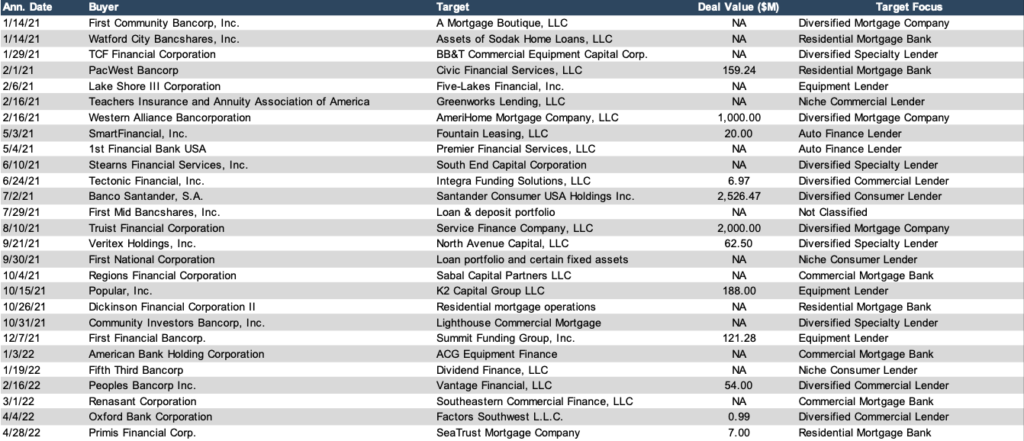
Specialty finance companies operate in a diverse landscape, catering to specific financial needs often underserved by traditional banks. These companies fill critical gaps in the market, providing tailored financial solutions to businesses and individuals. Understanding the various types of specialty finance companies, their products, and their target clients is essential for comprehending the breadth and depth of this industry.
Factoring Companies, Specialty finance company
Factoring companies provide short-term financing to businesses by purchasing their accounts receivable (invoices) at a discount. This allows businesses to access immediate cash flow, rather than waiting for customers to pay.
- Financial Products and Services: Factoring companies offer invoice factoring, where they purchase a company’s invoices, and sometimes provide credit protection against customer non-payment. They may also offer recourse or non-recourse factoring options.
- Target Clients: Factoring services are frequently utilized by small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), particularly those with a high volume of invoices and long payment cycles. Industries such as manufacturing, staffing, and transportation commonly use factoring.
- Transaction Sizes: Transaction sizes vary widely, from a few thousand dollars to several million, depending on the size of the business and the volume of invoices. The discount rate applied by the factoring company typically ranges from 1% to 5% or more, depending on the risk associated with the invoices and the client’s creditworthiness.
Equipment Finance Companies
Equipment finance companies specialize in providing financing for businesses to acquire equipment. This can include leasing or lending, enabling companies to access necessary assets without a large upfront capital outlay.
- Financial Products and Services: These companies offer equipment leases, equipment loans, and sale-leaseback agreements. They finance a broad range of equipment, including machinery, vehicles, and technology.
- Target Clients: Equipment finance companies serve businesses across various industries that require equipment for their operations. This includes construction, manufacturing, transportation, and healthcare.
- Transaction Sizes: Equipment financing transactions range from relatively small amounts for individual pieces of equipment to multi-million dollar deals for large-scale projects. Lease terms and loan durations are typically aligned with the useful life of the equipment.
Consumer Finance Companies
Consumer finance companies provide loans and other financial services directly to consumers. These companies often cater to individuals with limited access to traditional banking services.
- Financial Products and Services: They offer personal loans, auto loans, and installment loans. Some also provide credit cards and debt consolidation services.
- Target Clients: Consumer finance companies often serve individuals with less-than-perfect credit or those who require smaller loan amounts. These services can be particularly important for individuals lacking access to traditional financial institutions.
- Transaction Sizes: Loan amounts typically range from a few hundred dollars to tens of thousands, depending on the product and the borrower’s creditworthiness. Interest rates are often higher than those offered by traditional banks, reflecting the increased risk.
Comparing Specialty Finance Companies
The following table provides a comparison of the different types of specialty finance companies, highlighting their target clients and typical transaction sizes.
| Company Type | Financial Products and Services | Target Clients | Typical Transaction Sizes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Factoring Companies | Invoice factoring, recourse/non-recourse factoring | SMBs, particularly in manufacturing, staffing, and transportation | $1,000 – $1,000,000+ (or more, depending on the client’s size) |
| Equipment Finance Companies | Equipment leases, equipment loans, sale-leaseback agreements | Businesses in construction, manufacturing, transportation, and healthcare | $5,000 – $10,000,000+ (or more, depending on the equipment) |
| Consumer Finance Companies | Personal loans, auto loans, installment loans, credit cards | Individuals with less-than-perfect credit or those needing smaller loan amounts | $100 – $50,000+ (or more, depending on the product) |
Products and Services Offered
Specialty finance companies provide a diverse array of financial products and services designed to meet the specific needs of businesses that may not qualify for traditional bank loans. These offerings are crucial for businesses seeking flexible financing solutions, particularly those with unique asset structures or operating in industries with specific cash flow cycles. This section details the key products and services offered by specialty finance companies, including their typical terms, rates, and how they assist businesses.
Asset-Based Lending
Asset-based lending (ABL) is a financing method where a company secures a loan using its assets as collateral. These assets can include accounts receivable, inventory, equipment, and real estate. This approach allows businesses to access capital based on the value of their assets rather than solely on their credit history.
- Accounts Receivable Financing: This involves using a company’s outstanding invoices (accounts receivable) as collateral. The lender advances a percentage of the invoice value, typically 70-90%, providing immediate cash flow. The business repays the advance when the customer pays the invoice. Interest rates and fees are often calculated on a per-invoice basis or as a percentage of the outstanding balance. For example, a specialty finance company might charge a fee of 1.5% per month on the outstanding receivable balance.
- Inventory Financing: This type of financing uses a company’s inventory as collateral. It is often used by manufacturers, distributors, and retailers to finance the purchase or production of goods. The lender assesses the value and marketability of the inventory. Loan-to-value ratios (LTVs) can vary, often ranging from 50% to 70% of the inventory’s appraised value. Interest rates are typically tied to benchmarks like the prime rate, plus a margin. Fees may include origination fees, monitoring fees, and storage fees if the inventory is stored off-site.
- Equipment Financing: Businesses can finance the purchase of equipment, such as machinery, vehicles, or technology, using the equipment itself as collateral. This can take the form of a loan or a lease. Terms can range from a few years to a decade or more, depending on the equipment’s useful life. Interest rates vary based on the equipment type, creditworthiness, and the term of the financing. Fees might include application fees, documentation fees, and early payoff penalties.
- Real Estate Financing: Specialty finance companies may offer financing secured by commercial real estate. This can include mortgages, bridge loans, or construction financing. The terms, interest rates, and fees vary widely based on the property type, location, and the borrower’s financial strength. These loans often have longer terms and higher interest rates compared to other ABL products.
Invoice Financing
Invoice financing, also known as factoring, allows businesses to sell their outstanding invoices to a specialty finance company at a discount. The finance company then collects the payment from the customer. This provides immediate cash flow without taking on additional debt.
- Process: The business submits its invoices to the factoring company. The factoring company verifies the invoices and advances a percentage of the invoice value, typically 70-90%. The business uses the cash for its operational needs. The factoring company collects the payment from the customer. Once the invoice is paid, the factoring company remits the remaining balance, less its fees, to the business.
- Terms, Interest Rates, and Fees: Factoring fees are usually a percentage of the invoice value, ranging from 1% to 5% or more per invoice, depending on factors like the customer’s creditworthiness, the industry, and the invoice’s age. The term is typically the invoice’s payment period, such as 30, 60, or 90 days. Interest rates are not usually applied directly, but rather are incorporated into the factoring fee.
- Example: A business sells an invoice for $100,000 to a factoring company. The factoring company advances 80% ($80,000). The factoring company charges a fee of 3% of the invoice value. When the customer pays the invoice, the factoring company receives $100,000. It remits the remaining $17,000 ($100,000 – $80,000 – $3,000) to the business.
Merchant Cash Advances
A merchant cash advance (MCA) provides a lump sum of cash to a business in exchange for a percentage of its future credit card sales or, in some cases, debit card sales. This is a popular option for businesses with consistent credit card revenue.
- Process: The specialty finance company provides a lump sum to the business. The business repays the advance by allowing the finance company to collect a fixed percentage of its daily or weekly credit card sales. The repayment period is typically short-term, ranging from a few months to a couple of years.
- Terms, Interest Rates, and Fees: MCAs are not loans, so they don’t have interest rates in the traditional sense. Instead, they have a “factor rate,” which is a multiplier applied to the advance amount. For example, a factor rate of 1.2 means the business must repay 120% of the advance. Fees can include origination fees and processing fees. The factor rate and fees are generally higher than traditional loans, reflecting the higher risk and speed of access.
- Example: A business receives an MCA of $50,000 with a factor rate of 1.3. The business must repay $65,000 ($50,000 x 1.3). The finance company might collect 10% of the business’s daily credit card sales until the $65,000 is repaid.
How Specialty Finance Companies Help Businesses with Cash Flow Management
Specialty finance companies offer several key benefits to businesses in managing their cash flow, particularly for businesses that struggle to secure traditional financing.
- Faster Access to Capital: Compared to traditional bank loans, specialty finance companies often provide faster access to capital. This is crucial for businesses needing immediate funds to cover operational expenses, capitalize on opportunities, or manage unexpected financial challenges.
- Improved Working Capital: Products like invoice financing and asset-based lending directly improve working capital by converting assets (invoices, inventory) into readily available cash. This allows businesses to pay suppliers, meet payroll, and invest in growth without depleting their cash reserves.
- Flexibility and Customization: Specialty finance companies often offer more flexible and customized financing solutions than traditional banks. They are willing to tailor products to fit a business’s specific needs, asset base, and industry dynamics. This is particularly valuable for businesses with unique cash flow cycles or unconventional collateral.
- Reduced Reliance on Personal Guarantees: Asset-based lending, in particular, can reduce the reliance on personal guarantees, which are often required by traditional lenders. This can be beneficial for business owners who want to limit their personal financial risk.
- Focus on Assets, Not Just Creditworthiness: Unlike traditional lenders, specialty finance companies often focus on the value of a company’s assets when making lending decisions. This is beneficial for businesses that may have a weak credit history but possess valuable assets.
- Example: A seasonal retail business uses invoice financing to smooth out its cash flow. During the peak holiday season, the business generates a large volume of invoices. By factoring these invoices, the business receives immediate cash, allowing it to purchase inventory, hire seasonal staff, and fulfill customer orders without waiting for customer payments. This ensures the business can capitalize on the increased demand and maintain a healthy cash flow.
Target Markets and Industries

Specialty finance companies thrive by focusing on specific industries and target markets often underserved by traditional lenders. Their ability to understand the nuances of these sectors allows them to offer tailored financial solutions, manage risk effectively, and capitalize on market opportunities. This targeted approach differentiates them from broader financial institutions and fuels their success.
Industries Commonly Targeted by Specialty Finance Companies
Specialty finance companies often concentrate their efforts on sectors with unique financial needs or risk profiles. These industries frequently require specialized financial products that traditional banks are either unwilling or unable to provide.
- Real Estate: This sector is a significant focus, with specialty finance companies offering bridge loans, construction financing, and financing for distressed properties. These loans often cater to specific needs such as rapid funding for acquisitions or complex projects requiring customized financial structures.
- Healthcare: Healthcare is another prominent area. Specialty finance companies provide financing for medical equipment, practice acquisitions, and working capital for healthcare providers. The industry’s unique challenges, such as revenue cycle management and regulatory hurdles, make it a good fit for specialized financial solutions.
- Technology: The technology sector, especially startups and small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), often struggles to secure traditional financing. Specialty finance companies provide venture debt, equipment financing, and other tailored products to support these companies’ growth.
- Energy: Renewable energy projects, in particular, are often financed by specialty finance companies. They provide project financing, equipment leasing, and other financial solutions to support the development of solar, wind, and other clean energy initiatives.
- Transportation: Financing for aircraft, shipping, and trucking is often provided by specialty finance firms. They offer leasing, asset-based lending, and other specialized financial products tailored to the needs of these industries.
- Manufacturing: Equipment financing, working capital loans, and other financial products are often provided to manufacturing companies. These specialized loans help companies acquire new equipment, manage inventory, and fund other operational needs.
- Franchising: Financing for franchise development, including acquisition and build-out costs, is often a focus. Specialty finance companies understand the unique financial needs and risk profiles of franchisees.
Factors Making Industries Suitable for Specialty Financing
Several factors contribute to the suitability of an industry for specialty financing. These factors influence the risk-reward profile and the ability of specialty finance companies to create value.
- Industry-Specific Expertise: A deep understanding of the industry’s dynamics, regulations, and market trends is crucial. This expertise allows specialty finance companies to assess risk more accurately and structure financial products that meet specific needs.
- Asset-Based Lending Opportunities: Industries with tangible assets, such as equipment, real estate, or inventory, are often attractive. These assets can serve as collateral, reducing the lender’s risk and enabling more flexible financing terms.
- High Growth Potential: Industries experiencing rapid growth often require significant capital. Specialty finance companies can capitalize on these opportunities by providing funding to fuel expansion.
- Underserved Markets: Industries where traditional lenders are less active or offer less competitive financing options are prime targets. This creates an opportunity for specialty finance companies to fill the void and provide valuable services.
- Complex Financial Needs: Industries with intricate financial requirements, such as project financing or structured finance, are well-suited for specialty financing. These complex needs often require customized solutions.
Tailoring Services to Different Industries
Specialty finance companies customize their services to meet the specific needs of their target industries. This customization involves understanding the industry’s unique challenges, risk factors, and financial requirements.
- Real Estate: Specialty finance companies may offer bridge loans with short-term financing to quickly secure a property. They might also provide construction loans tailored to specific project phases, with disbursements based on progress. For example, a company specializing in real estate might offer a bridge loan to a developer to quickly acquire a property before securing permanent financing, allowing them to capitalize on an opportunity before it disappears.
- Healthcare: A specialty finance company might offer equipment financing with flexible payment terms aligned with the revenue cycle of medical practices. They might also provide working capital loans to address the challenges of delayed insurance reimbursements. For instance, a specialty finance company may offer a medical practice a loan to purchase new MRI equipment, with payments structured to coincide with the practice’s revenue generated from the equipment.
- Technology: For technology companies, specialty finance companies might provide venture debt, which is debt financing that is subordinate to venture capital equity. This type of financing helps to avoid diluting equity, providing a more advantageous solution. For example, a SaaS startup might secure a venture debt facility to fund its marketing and sales efforts, allowing them to accelerate customer acquisition without issuing more equity.
- Energy: Specialty finance companies can provide project financing for renewable energy projects, structuring loans with terms that align with the project’s revenue stream. They may also offer equipment leasing for solar panels or wind turbines. A specialty finance company might offer a loan to a solar farm, with repayment terms based on the projected revenue generated from the sale of electricity, helping to support the transition to renewable energy.
- Transportation: In the transportation sector, specialty finance companies might provide aircraft leasing with tailored payment schedules that reflect seasonal demand or equipment financing for trucking fleets. For example, a specialty finance company might provide financing for a trucking company to acquire a fleet of new trucks, with loan terms and payments structured to accommodate the company’s cash flow and operational needs.
The Lending Process
Specialty finance companies operate with a distinct lending process tailored to the unique needs of their target markets. This process is typically more flexible and faster than traditional bank lending, allowing for quicker access to capital. Understanding this process is crucial for both borrowers and investors involved with specialty finance.
Typical Steps in the Lending Process
The lending process generally follows a series of defined steps, designed to assess the borrower’s creditworthiness and the viability of the financing request. These steps ensure that the specialty finance company manages risk effectively while providing timely funding.
- Application and Initial Screening: The process begins with a loan application submitted by the borrower. This application includes financial statements, business plans, and other relevant documentation. The specialty finance company conducts an initial screening to determine if the application meets its basic lending criteria.
- Due Diligence: This involves a thorough investigation of the borrower’s financial health, business operations, and credit history. Due diligence aims to verify the information provided in the application and assess the overall risk associated with the loan.
- Underwriting and Credit Analysis: The underwriting process involves a detailed analysis of the borrower’s ability to repay the loan. This includes assessing cash flow, collateral (if any), and the overall financial stability of the business. The credit analysis determines the loan terms, interest rates, and any required covenants.
- Loan Approval and Documentation: If the loan is approved, the specialty finance company prepares loan documents that Artikel the terms and conditions of the financing. Both the lender and the borrower sign these documents, formalizing the loan agreement.
- Funding: After the loan documents are signed, the funds are disbursed to the borrower. The disbursement process is typically swift, especially compared to traditional bank loans.
- Loan Servicing and Monitoring: Once the loan is funded, the specialty finance company monitors the borrower’s performance and repayment schedule. This may involve ongoing financial reporting and periodic reviews to ensure the loan is performing as expected.
Due Diligence Procedures
Due diligence is a critical phase in the lending process, allowing specialty finance companies to mitigate risk and make informed lending decisions. The depth of due diligence varies depending on the size and type of loan, but certain procedures are standard across the industry.
- Financial Statement Analysis: Reviewing the borrower’s financial statements (income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements) to assess profitability, liquidity, and solvency. Key metrics, such as the debt-to-equity ratio and current ratio, are carefully examined.
- Credit Report Review: Obtaining and analyzing credit reports to assess the borrower’s credit history, including payment behavior and outstanding debts. This provides insights into the borrower’s past financial performance.
- Verification of Assets: Verifying the existence and value of any collateral offered, such as equipment, real estate, or accounts receivable. This ensures the collateral is sufficient to cover the loan in case of default.
- Industry Analysis: Evaluating the borrower’s industry to understand market trends, competitive landscape, and potential risks. This provides context for the borrower’s business performance and prospects.
- Management Interviews: Conducting interviews with the borrower’s management team to assess their experience, expertise, and the overall quality of their operations. This offers insights into the borrower’s business strategies and risk management practices.
Risk Assessment and Credit Limit Setting
Specialty finance companies are experts at assessing risk, which is crucial for determining loan terms and setting credit limits. Their risk assessment process is highly refined, incorporating various factors to evaluate a borrower’s creditworthiness.
Specialty finance company – The assessment involves the following key considerations:
- Credit Scoring: Specialty finance companies often use credit scoring models, incorporating data from credit reports and other sources to assign a credit score. This score helps to quickly assess the borrower’s creditworthiness.
- Cash Flow Analysis: Analyzing the borrower’s cash flow to determine their ability to repay the loan. This involves projecting future cash flows and assessing the stability and predictability of these cash flows.
- Collateral Evaluation: Evaluating the value and liquidity of any collateral offered to secure the loan. The collateral serves as a safeguard for the lender in case of default.
- Industry Risk Assessment: Assessing the risks associated with the borrower’s industry. Industries with higher volatility or cyclicality may require stricter lending terms.
- Setting Credit Limits: Based on the risk assessment, the specialty finance company sets credit limits, which determine the maximum amount of financing available to the borrower. The credit limit is often tied to the borrower’s creditworthiness and the availability of collateral.
For example, a factoring company might use the following formula to assess the credit limit:
Credit Limit = (Eligible Accounts Receivable) * (Advance Rate) – (Reserve)
Where:
- Eligible Accounts Receivable represents the value of the accounts receivable that meet the factoring company’s criteria.
- Advance Rate is the percentage of the accounts receivable the company is willing to advance to the borrower.
- Reserve is a percentage withheld by the factoring company to cover potential deductions, disputes, or credit losses.
Advantages of Specialty Finance
Specialty finance companies offer unique advantages over traditional financing methods, particularly for businesses with specific needs or challenges. These advantages often translate to increased flexibility, faster access to capital, and tailored solutions that can be instrumental in driving growth and navigating financial hurdles. The ability to secure financing that aligns with a company’s specific circumstances is a key differentiator.
Tailored Financing Solutions
Specialty finance companies excel at providing financing solutions that are customized to the specific needs of a business, unlike traditional lenders that often offer standardized products. This customization is a significant advantage, allowing businesses to secure funding that aligns perfectly with their financial situation, industry, and growth objectives.
- Industry-Specific Expertise: Many specialty finance companies have deep expertise in particular industries. This allows them to understand the nuances and challenges faced by businesses within those sectors, enabling them to offer more relevant and effective financing options. For example, a company specializing in financing for the construction industry would understand the unique needs of construction businesses, such as project-based financing and equipment leasing, much better than a general bank.
- Flexible Loan Structures: Specialty finance companies often offer more flexible loan structures than traditional lenders. This can include adjustable repayment schedules, interest-only periods, or balloon payments, allowing businesses to tailor their financing to their cash flow patterns. A growing startup might benefit from an interest-only period during its initial growth phase, allowing it to conserve capital.
- Non-Traditional Collateral: Specialty finance companies are often willing to consider non-traditional forms of collateral, such as intellectual property, accounts receivable, or future revenue streams. This can be crucial for businesses that lack traditional assets or have limited credit histories. A software company, for example, might secure financing based on the value of its proprietary software and future subscription revenue.
Faster Access to Capital
One of the most significant advantages of specialty finance is the speed with which businesses can access capital. Traditional lending processes can be lengthy and cumbersome, often requiring extensive documentation, credit checks, and underwriting procedures. Specialty finance companies, on the other hand, are often able to provide funding much more quickly.
- Streamlined Application Processes: Specialty finance companies typically have streamlined application processes compared to traditional banks. This can involve simpler documentation requirements and faster approval times. This can be particularly advantageous for businesses that need capital quickly to seize opportunities or address urgent financial needs.
- Faster Decision-Making: Specialty finance companies often have more streamlined decision-making processes, allowing them to make quicker funding decisions. This is often due to their specialization and in-depth understanding of the industries they serve. A business that needs funds to cover a sudden inventory purchase can often receive a decision from a specialty finance company within days, compared to weeks or months with a traditional bank.
- Reduced Bureaucracy: The reduced bureaucracy associated with specialty finance can expedite the funding process. This can be particularly helpful for businesses that are time-sensitive or need to act quickly to capitalize on market opportunities.
Support for Growth and Overcoming Financial Challenges
Specialty finance can be a powerful tool for businesses seeking to grow or overcome financial challenges. They often provide solutions that traditional lenders are unable or unwilling to offer, particularly for businesses with unique circumstances or risk profiles.
- Funding for Growth Initiatives: Specialty finance can provide capital for a wide range of growth initiatives, such as expanding operations, launching new products, or entering new markets. A retail business, for example, could use specialty financing to fund the opening of a new store location.
- Bridge Financing: Specialty finance companies can offer bridge financing to help businesses navigate temporary financial difficulties, such as a delay in receiving payments from customers or a seasonal downturn in sales. This can help businesses maintain operations and avoid disruptions.
- Debt Restructuring: Some specialty finance companies specialize in debt restructuring, helping businesses to manage and reorganize their existing debt obligations. This can involve consolidating debt, negotiating more favorable repayment terms, or providing additional capital to improve financial stability.
Risks and Challenges
Specialty finance companies operate in a landscape fraught with inherent risks. Understanding and proactively managing these challenges is crucial for their survival and success. The following sections delve into the key risks, regulatory hurdles, and mitigation strategies employed by these specialized financial institutions.
High Interest Rates and Collateral Requirements
Specialty finance often entails higher interest rates and stricter collateral requirements compared to traditional lending. This is a direct consequence of the increased risk profile associated with the borrowers and the types of assets financed.
- Higher Interest Rates: These rates reflect the elevated risk of default. Specialty finance companies often cater to borrowers deemed riskier by conventional lenders, such as small businesses with limited credit history or those seeking financing for specialized assets. For example, a construction equipment financing company might charge a higher interest rate than a bank providing a mortgage.
- Collateral Requirements: Robust collateral is essential to mitigate the risk of loss. Specialty finance companies frequently require collateral, which can include the financed asset itself (e.g., equipment, inventory, accounts receivable), real estate, or other valuable assets. The value and liquidity of the collateral are critical considerations.
- Impact on Borrowers: While high rates and strict collateral can provide access to capital, they also place a significant burden on borrowers. The increased cost of borrowing can strain cash flow, potentially leading to financial distress if the business fails to generate sufficient revenue to service the debt.
- Example: A company specializing in financing for film productions might require the film itself as collateral, along with personal guarantees from the producers. The interest rates would reflect the high risk associated with the project’s success.
Regulatory Environment and Compliance Requirements
Specialty finance companies are subject to a complex web of regulations designed to protect consumers, ensure fair lending practices, and maintain the stability of the financial system. Compliance with these regulations is an ongoing and resource-intensive undertaking.
- Federal Regulations: The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) oversees many aspects of consumer lending, including truth-in-lending disclosures, fair lending practices, and debt collection practices. Other federal agencies, such as the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), also have oversight responsibilities.
- State Regulations: State laws can vary significantly, adding complexity. These laws often govern licensing requirements, interest rate caps, and other specific aspects of lending within the state.
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC): Specialty finance companies are required to implement AML and KYC procedures to prevent financial crimes, including money laundering and terrorist financing. This involves verifying customer identities, monitoring transactions, and reporting suspicious activity.
- Data Privacy and Security: Compliance with data privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), is crucial to protect sensitive customer information.
- Consequences of Non-Compliance: Failure to comply with regulations can result in significant penalties, including fines, legal action, and reputational damage. This can severely impact a specialty finance company’s ability to operate.
Risk Management and Mitigation Strategies
Specialty finance companies employ various strategies to manage and mitigate the inherent risks in their operations. These strategies are essential for maintaining profitability and ensuring long-term sustainability.
- Due Diligence: Thorough due diligence on borrowers and collateral is paramount. This involves a comprehensive assessment of the borrower’s creditworthiness, business plan, and the value and condition of the collateral.
- Risk-Based Pricing: Interest rates and fees should be carefully calibrated to reflect the level of risk associated with each loan. This ensures that higher-risk borrowers pay a premium that compensates for the increased probability of default.
- Diversification: Diversifying the loan portfolio across different industries, geographies, and borrower types can reduce the impact of any single default.
- Collateral Management: Establishing robust procedures for valuing, monitoring, and managing collateral is essential. This includes regular inspections, insurance requirements, and prompt action in case of default.
- Credit Scoring and Underwriting Models: Employing sophisticated credit scoring models and underwriting processes helps assess risk more accurately and consistently.
- Stress Testing: Regularly stress-testing the loan portfolio under various economic scenarios helps assess the company’s resilience to adverse conditions.
- Insurance and Hedging: Utilizing insurance products (e.g., credit insurance) and hedging strategies can help mitigate certain risks, such as losses from defaults or fluctuations in interest rates.
- Example: A factoring company might use credit insurance to protect against losses from customer defaults on accounts receivable.
Regulatory Landscape
The specialty finance industry operates within a complex regulatory environment. Understanding and adhering to these regulations is crucial for the success and sustainability of any specialty finance company. This section Artikels the key regulatory bodies, compliance requirements, and the impact of regulatory changes on the industry.
Main Regulatory Bodies
Specialty finance companies are subject to oversight from various regulatory bodies at both the federal and state levels. The specific bodies involved depend on the type of financial products offered and the geographic scope of the company’s operations. These regulatory bodies work to ensure fair lending practices, protect consumers, and maintain the stability of the financial system.
- Federal Regulatory Bodies: These bodies often oversee broader financial practices and set the stage for state-level regulations.
- The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB): The CFPB is responsible for regulating consumer financial products and services. It enforces federal consumer financial laws, including those related to lending, and has the authority to examine and supervise financial institutions, including some specialty finance companies, to ensure compliance. The CFPB’s oversight is especially relevant for companies offering consumer-facing financial products.
- The Federal Trade Commission (FTC): The FTC enforces federal laws related to consumer protection and competition. It has jurisdiction over deceptive or unfair business practices, including those related to lending. The FTC investigates and prosecutes companies that violate these laws, which can result in significant penalties.
- The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC): The SEC regulates the securities markets and protects investors. Specialty finance companies that issue securities, such as bonds or stock, are subject to SEC regulations, including registration requirements and disclosure obligations.
- The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC): While not directly regulating most specialty finance companies, the FDIC insures deposits in banks and thrifts. Specialty finance companies may interact with FDIC-insured institutions, and therefore, must be aware of the regulations affecting those institutions.
- State Regulatory Bodies: State-level regulations often provide more specific rules tailored to local market conditions.
- State Banking Departments/Financial Institutions Divisions: These departments are responsible for licensing and supervising financial institutions within their state. They regulate state-chartered banks, credit unions, and other financial service providers, including certain types of specialty finance companies. State regulators often focus on consumer protection, financial stability, and fair lending practices.
- State Attorney Generals: State Attorneys General have the authority to enforce consumer protection laws and investigate fraudulent or deceptive business practices. They can bring lawsuits against specialty finance companies that violate state laws, leading to fines, injunctions, and other penalties.
- State Securities Regulators: Similar to the SEC at the federal level, state securities regulators oversee the offering and sale of securities within their state. Specialty finance companies issuing securities must comply with state securities laws, including registration and disclosure requirements.
Compliance Requirements
Specialty finance companies must adhere to a wide range of compliance requirements to operate legally and ethically. These requirements cover various aspects of their business, from lending practices to data security. Strict adherence to these regulations is not only legally mandated but also builds trust with customers and investors.
- Fair Lending Laws: These laws prohibit discrimination in lending based on factors such as race, religion, sex, national origin, and other protected characteristics.
- The Equal Credit Opportunity Act (ECOA): ECOA prohibits discrimination in any aspect of a credit transaction. This includes the application process, credit decisions, and terms of credit. Specialty finance companies must ensure their lending practices comply with ECOA.
- The Fair Housing Act: While primarily focused on housing, this act also prohibits discrimination in lending related to housing. Specialty finance companies involved in mortgage lending must comply with the Fair Housing Act.
- The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA): FCRA regulates the collection, use, and disclosure of consumer credit information. Specialty finance companies must comply with FCRA when obtaining and using credit reports.
- Truth in Lending Act (TILA): TILA requires lenders to disclose the terms and costs of credit to borrowers.
- Disclosure Requirements: Specialty finance companies must provide borrowers with clear and concise information about the loan, including the interest rate, fees, and repayment schedule.
- Advertising Regulations: TILA also regulates the advertising of credit products. Companies must ensure their advertisements are accurate and do not mislead consumers.
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) Regulations: These regulations are designed to prevent financial crimes, such as money laundering and terrorist financing.
- Customer Identification Programs (CIP): Specialty finance companies must establish CIPs to verify the identity of their customers. This typically involves collecting identifying information and verifying it against government databases.
- Suspicious Activity Reporting (SAR): Companies must report suspicious activity to the relevant authorities, such as the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN).
- Data Privacy and Security Regulations: Specialty finance companies handle sensitive customer data, making data privacy and security compliance critical.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) (for international operations): If a specialty finance company operates internationally, it must comply with GDPR, which sets strict rules for the collection, use, and storage of personal data.
- The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) (for operations in California): CCPA grants California consumers certain rights regarding their personal data, including the right to know what data is collected, the right to delete their data, and the right to opt-out of the sale of their data.
- Data Security Measures: Companies must implement robust data security measures to protect customer data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. This includes using encryption, implementing firewalls, and conducting regular security audits.
- Licensing and Registration: Many specialty finance activities require specific licenses or registrations at the state level.
- Lender Licenses: Companies that provide loans typically need a lender license from the state in which they operate.
- Debt Collection Licenses: Companies that engage in debt collection must obtain a debt collection license.
- Money Transmitter Licenses: Companies that transmit money must obtain a money transmitter license.
Impact of Regulatory Changes
Regulatory changes can significantly impact the specialty finance industry, affecting its operations, profitability, and overall landscape. Changes can be driven by economic conditions, political shifts, and technological advancements. Specialty finance companies must stay informed and adapt to these changes to remain compliant and competitive.
- Increased Compliance Costs: New regulations often require companies to invest in new systems, processes, and personnel to ensure compliance.
- Example: The implementation of new data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, has led to increased costs for specialty finance companies to upgrade their data security systems, train employees, and hire compliance officers.
- Changes in Product Offerings: Regulations can limit the types of financial products a company can offer or the terms on which they can be offered.
- Example: Regulations on payday loans have limited the terms and interest rates that these loans can have, which has changed the business models of companies offering these products.
- Impact on Profitability: Compliance costs and restrictions on product offerings can reduce profitability.
- Example: Stricter regulations on the fees and interest rates that specialty finance companies can charge can reduce their profit margins.
- Increased Scrutiny and Enforcement: Regulatory changes often lead to increased scrutiny from regulators, including more frequent examinations and stricter enforcement actions.
- Example: Following the 2008 financial crisis, regulators increased their scrutiny of mortgage lenders, leading to stricter enforcement of lending standards and increased penalties for non-compliance.
- Market Consolidation: The cost of compliance can be particularly challenging for smaller companies, potentially leading to market consolidation as smaller players are acquired by larger firms.
- Example: The increased regulatory burden on community banks has led to a wave of mergers and acquisitions in the banking industry.
- Innovation and Adaptation: Regulatory changes can also drive innovation as companies seek to develop new products and services that comply with the new rules.
- Example: The rise of fintech companies has been driven in part by regulatory changes that have created opportunities for new business models and technologies in the financial services industry.
Technological Advancements
Technology is fundamentally reshaping the specialty finance landscape, driving efficiency, expanding reach, and enhancing the overall customer experience. The industry’s adoption of new technologies is accelerating, fueled by the need to remain competitive and meet evolving market demands. This transformation is particularly evident in how specialty finance companies assess risk, manage operations, and interact with clients.
The Impact of Technology on Specialty Finance
Technological advancements are providing specialty finance companies with powerful tools to streamline operations, improve decision-making, and offer more tailored financial solutions. This includes automation, data analytics, and enhanced communication platforms.
The Role of Fintech in Specialized Financial Services
Fintech, or financial technology, plays a critical role in delivering specialized financial services. Fintech companies are developing innovative solutions that address the unique needs of specific market segments, often by leveraging the power of data, artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud computing. This results in improved accessibility, faster processing times, and reduced costs.
- Automated Underwriting: Fintech platforms are using AI and machine learning to automate the loan underwriting process. These systems can analyze vast amounts of data, including credit history, financial statements, and alternative data sources, to assess risk and make faster lending decisions. For example, companies like Kabbage (now part of American Express) utilized automated underwriting to provide small business loans quickly.
- Digital Lending Platforms: Fintech has enabled the creation of online lending platforms that connect borrowers directly with lenders. These platforms offer a more streamlined and transparent borrowing experience compared to traditional methods. LendingClub and Prosper are examples of peer-to-peer lending platforms that have disrupted the personal loan market.
- Data Analytics and Risk Management: Advanced data analytics tools are enabling specialty finance companies to better understand their customers, identify potential risks, and optimize their portfolios. By analyzing historical data, market trends, and economic indicators, companies can make more informed lending decisions and mitigate losses.
- Blockchain Technology: While still in its early stages, blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize various aspects of specialty finance, including payments, trade finance, and supply chain financing. Blockchain can improve transparency, reduce fraud, and streamline transactions.
- Mobile Applications and Customer Portals: Specialty finance companies are developing mobile apps and online portals to provide customers with convenient access to their accounts, loan information, and payment options. These platforms enhance the customer experience and improve communication.
Technology’s Impact on Efficiency and Customer Experience
Specialty finance companies are utilizing technology to enhance efficiency and provide a better customer experience. Automation, data analytics, and improved communication tools are key components of this transformation.
- Streamlined Loan Processing: Automation of tasks such as document collection, verification, and credit scoring significantly reduces processing times. This results in faster loan approvals and a more efficient lending process.
- Improved Risk Assessment: Data analytics and AI enable more accurate risk assessment, allowing companies to better evaluate borrowers and tailor loan terms to their specific needs.
- Enhanced Customer Service: Chatbots, online portals, and mobile apps provide customers with instant access to information, support, and account management tools. This improves customer satisfaction and reduces the need for manual intervention.
- Personalized Financial Products: Technology enables specialty finance companies to offer more customized financial products and services that are tailored to the unique needs of their customers.
- Expanded Market Reach: Online platforms and digital marketing strategies allow specialty finance companies to reach a wider audience, including customers who may not have access to traditional financial services.
Comparison with Traditional Banks
Specialty finance companies and traditional banks both offer financial services, but they cater to different needs and operate with distinct approaches. Understanding the key differences between these two types of financial institutions is crucial for businesses and individuals seeking financing. While banks remain the cornerstone of the financial system, specialty finance companies provide a valuable alternative, particularly for those with unique needs or circumstances.
Divergent Service Models
Traditional banks typically offer a wide range of financial products and services to a broad customer base, including individuals, small businesses, and large corporations. Their operations are often highly regulated and standardized, focusing on established creditworthiness and lower-risk lending. Specialty finance companies, on the other hand, concentrate on specific niches or underserved markets. This specialization allows them to develop expertise and offer tailored solutions that traditional banks might not provide.
Situations Favoring Specialty Finance
A specialty finance company might be a more suitable option than a traditional bank in several scenarios.
- Unique Financing Needs: When a business requires financing for a specialized purpose, such as equipment leasing, factoring, or film financing, a specialty finance company with expertise in that area can provide more flexible and customized solutions.
- Credit Challenges: Businesses with less-than-perfect credit or limited operating history may find it difficult to secure financing from traditional banks. Specialty finance companies often have more flexible underwriting criteria and may be willing to take on higher-risk borrowers.
- Speed and Efficiency: Specialty finance companies can often provide faster approval processes and quicker access to funds compared to traditional banks. This is particularly important for businesses needing immediate capital.
- Industry Specialization: Specialty finance companies often understand the specific needs and challenges of particular industries. This allows them to offer financing solutions tailored to the unique requirements of those sectors.
Key Differences: Specialty Finance vs. Traditional Banks
The following table Artikels the key differences between specialty finance companies and traditional banks:
| Feature | Specialty Finance Company | Traditional Bank | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target Market | Specific industries, underserved markets, or niche financing needs. | Broad customer base, including individuals, small businesses, and large corporations. | Equipment leasing for construction companies; factoring for textile manufacturers. |
| Loan Types | Specialized financing products like equipment leasing, factoring, invoice financing, merchant cash advances, and film financing. | A wide range of loan products, including commercial loans, mortgages, personal loans, and lines of credit. | Commercial real estate loans; home mortgages; personal loans. |
| Approval Processes | Often more flexible and quicker, with a focus on specific industry expertise and collateral. | More standardized and typically involve extensive credit checks, financial statements, and collateral evaluations. | Detailed credit analysis, verification of income, and appraisal of collateral. |
| Risk Appetite | Often higher risk appetite, willing to finance borrowers with less-than-perfect credit or unique financing needs. | Generally lower risk appetite, focusing on established creditworthiness and lower-risk lending. | Loans to startups; loans to borrowers with limited credit history. |
Case Studies
Specialty finance companies often play a crucial role in fueling business growth and providing tailored financial solutions that traditional banks might overlook. Examining real-world case studies allows us to understand the practical application of these financial instruments and the tangible benefits they offer. This section will delve into several examples, highlighting the specific financial solutions provided and the positive outcomes achieved by businesses across diverse industries.
Manufacturing Company Expansion
A manufacturing company, “Precision Engineering,” specializing in advanced components, sought to expand its production capacity. They needed significant capital to purchase new machinery and upgrade their existing facilities.
Precision Engineering secured a term loan from a specialty finance company specializing in asset-based lending. The loan was secured by the company’s existing equipment and inventory.
- The specialty finance company assessed the value of Precision Engineering’s assets and provided a loan based on a percentage of their appraised value.
- This allowed Precision Engineering to avoid diluting equity or taking on excessive debt from traditional lenders who might have been hesitant due to the industry’s cyclical nature.
- The loan terms were structured to align with the company’s cash flow projections, providing flexibility in repayment.
The positive outcomes included:
- Increased production capacity by 40% within one year.
- A 25% rise in revenue, driven by the ability to fulfill larger orders.
- Enhanced operational efficiency through the implementation of new technologies.
Technology Startup Funding
A technology startup, “InnovateTech,” developing a new software solution, required funding to cover research and development costs, marketing expenses, and initial staffing. Traditional banks were reluctant to provide loans due to the inherent risks associated with early-stage technology companies.
InnovateTech obtained venture debt from a specialty finance company focused on the technology sector. This debt was structured with warrants, allowing the finance company to participate in the company’s future success.
- The specialty finance company conducted thorough due diligence, evaluating the company’s technology, market potential, and management team.
- The venture debt provided the necessary capital without forcing the founders to relinquish significant equity in the early stages.
- The warrants offered the finance company the opportunity to benefit from the company’s growth, aligning their interests with InnovateTech’s success.
The positive outcomes included:
- Successful launch of the software product within the projected timeframe.
- Significant customer acquisition and market penetration.
- Attracting additional investment rounds from venture capital firms, increasing the company’s valuation.
Healthcare Practice Acquisition
A medical practice, “Apex Medical Group,” aimed to acquire a smaller, competing practice to expand its patient base and service offerings. Securing financing from a traditional bank proved challenging due to the complexities of valuing healthcare practices and the specific regulatory environment.
Apex Medical Group utilized a specialty finance company specializing in healthcare financing. The finance company provided a loan specifically designed for acquisitions within the healthcare sector.
- The specialty finance company had expertise in evaluating the financial performance of healthcare practices, including revenue cycles, patient demographics, and regulatory compliance.
- The loan was structured to accommodate the unique cash flow dynamics of the healthcare industry, with flexible repayment terms.
- The finance company provided guidance and support throughout the acquisition process, helping Apex Medical Group navigate the complexities of the transaction.
The positive outcomes included:
- Successful acquisition of the target practice, doubling the patient base.
- Expansion of service offerings, leading to increased revenue streams.
- Enhanced operational efficiency through the integration of the two practices.
Real Estate Development Project
A real estate developer, “Skyline Properties,” needed funding for a large-scale residential development project. Traditional banks were hesitant to provide the entire amount due to the project’s risk profile and the length of the construction timeline.
Skyline Properties secured a construction loan from a specialty finance company specializing in real estate financing. This loan was structured to disburse funds in stages, aligned with the project’s milestones.
- The specialty finance company conducted a thorough assessment of the project’s feasibility, including market analysis, construction costs, and projected sales.
- The loan was structured with flexible draw schedules, allowing Skyline Properties to access funds as needed throughout the construction process.
- The finance company provided ongoing monitoring and support, ensuring the project stayed on track and within budget.
The positive outcomes included:
- Successful completion of the residential development project within the projected timeframe.
- Strong sales performance, generating significant profits for Skyline Properties.
- Enhanced reputation and credibility within the real estate development industry.
Future Trends
The specialty finance industry is dynamic and constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, shifts in economic conditions, and evolving consumer and business needs. Understanding these future trends is crucial for specialty finance companies to remain competitive and capitalize on emerging opportunities. This section explores some of the most significant trends shaping the future of specialty finance, examining their potential impacts and the opportunities they present.
Technological Disruption and Innovation
Technological advancements are at the forefront of transforming the specialty finance landscape. Fintech companies and traditional players are leveraging technology to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and enhance customer experiences.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are increasingly being used for credit scoring, fraud detection, and automated underwriting. These technologies enable faster decision-making, reduced operational costs, and improved risk management. For instance, AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and predict creditworthiness more accurately than traditional methods.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain has the potential to revolutionize various aspects of specialty finance, including loan origination, securitization, and payment processing. Its decentralized and transparent nature can reduce fraud, increase efficiency, and enhance security. Smart contracts, built on blockchain, can automate loan disbursement and repayment, reducing administrative burdens.
- Digital Lending Platforms: Online lending platforms are becoming more prevalent, offering faster and more convenient access to capital. These platforms often utilize data analytics and automation to streamline the application and approval processes. This shift towards digital lending is particularly appealing to borrowers seeking quick and efficient financing solutions.
- Automation and Process Optimization: Automation tools are being implemented across various functions, from customer onboarding to loan servicing. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human employees to focus on more strategic activities.
Changing Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory environment for specialty finance is continuously evolving, with new regulations and guidelines emerging to address risks and protect consumers. Staying compliant with these changes is critical for businesses to operate successfully.
- Increased Scrutiny: Regulators are paying closer attention to the specialty finance industry, particularly in areas such as consumer protection, fair lending practices, and data privacy. This increased scrutiny can lead to stricter compliance requirements and potential penalties for non-compliance.
- Data Privacy Regulations: Regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) are impacting how specialty finance companies collect, store, and use customer data. Companies must implement robust data protection measures to comply with these regulations and protect sensitive information.
- Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Considerations: ESG factors are gaining importance in investment decisions and lending practices. Specialty finance companies may face increasing pressure to integrate ESG considerations into their lending criteria and operations.
Evolving Market Dynamics
The specialty finance market is influenced by broader economic trends, shifting consumer preferences, and the emergence of new industries.
- Growth in Specific Sectors: Certain sectors, such as renewable energy, healthcare, and technology, are experiencing significant growth, creating new opportunities for specialty finance companies. Providing financing solutions tailored to the needs of these industries can lead to substantial growth.
- Demand for Flexible Financing: Businesses and consumers are increasingly seeking flexible financing options that can adapt to their specific needs. This includes products such as revenue-based financing, which aligns repayment with revenue performance, and customized loan structures.
- Rise of the Gig Economy: The gig economy continues to expand, creating a demand for financing solutions tailored to freelancers and independent contractors. Specialty finance companies can offer products such as invoice factoring and working capital loans to support the financial needs of this growing segment.
- Impact of Inflation and Interest Rate Fluctuations: Inflation and interest rate changes can significantly impact the cost of borrowing and the overall economic climate. Specialty finance companies must carefully manage their interest rate risk and adjust their lending strategies accordingly.
Emerging Opportunities
These trends are creating new opportunities for specialty finance companies to innovate and expand their offerings.
- Niche Market Specialization: Focusing on specific underserved markets or industries can provide a competitive advantage. Companies can develop specialized expertise and tailor their products to meet the unique needs of these segments.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborating with fintech companies, technology providers, and other financial institutions can provide access to new technologies, distribution channels, and customer bases.
- Product Diversification: Expanding the range of financial products and services offered can attract a broader customer base and increase revenue streams. This could include offering a mix of lending products, leasing options, and other financial solutions.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Leveraging data analytics to improve risk assessment, customer acquisition, and loan performance can enhance profitability and competitiveness.
Building a Successful Specialty Finance Company
Starting and growing a specialty finance company requires a strategic approach, a deep understanding of the target market, and a commitment to building strong relationships. Success in this industry hinges on navigating complex regulations, managing risk effectively, and leveraging technological advancements to gain a competitive edge. This section Artikels the key steps, essential skills, resources, and relationship-building strategies critical for achieving sustainable growth.
Key Steps in Starting and Growing a Specialty Finance Company
The journey to building a successful specialty finance company involves several crucial phases. These steps, when executed strategically, lay the foundation for long-term viability and growth.
- Market Research and Niche Selection: Thorough market research is the cornerstone of any successful specialty finance venture. It involves identifying a specific underserved niche or industry with unmet financial needs. This process entails analyzing market trends, assessing the competitive landscape, and evaluating the potential profitability of various financing options. For example, a company might focus on providing financing for renewable energy projects, leveraging the growing demand for sustainable energy solutions.
- Developing a Business Plan: A comprehensive business plan serves as the roadmap for the company. It should Artikel the company’s mission, vision, target market, products and services, marketing strategy, financial projections, and management team. The plan should also include a detailed risk assessment and mitigation strategy. This includes understanding the types of collateral and how to manage them in case of default.
- Securing Funding: Capital is essential to start and grow a specialty finance company. Funding sources can include private equity investors, venture capital firms, institutional investors, and debt financing from banks or other financial institutions. The specific funding strategy will depend on the company’s business model, growth projections, and risk profile.
- Obtaining Licenses and Regulatory Compliance: Navigating the regulatory landscape is crucial. Specialty finance companies are subject to various federal, state, and local regulations. Obtaining the necessary licenses and permits is essential for legal operation. Compliance with these regulations, including those related to lending practices, consumer protection, and anti-money laundering, is ongoing.
- Building a Strong Team: Assembling a skilled and experienced team is critical for success. This team should include professionals with expertise in finance, credit analysis, risk management, legal, and sales. Hiring the right people with industry-specific knowledge is crucial.
- Establishing Operational Infrastructure: Setting up efficient operational systems is essential for managing loan origination, servicing, and collections. This includes implementing loan origination software, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and robust data security protocols. Automating these processes improves efficiency and reduces operational costs.
- Developing a Marketing and Sales Strategy: A well-defined marketing and sales strategy is essential for attracting clients and generating loan volume. This strategy should include identifying the target market, developing a strong brand identity, and utilizing various marketing channels, such as online advertising, industry events, and partnerships.
- Managing Risk and Portfolio Performance: Effective risk management is crucial for long-term success. This involves developing and implementing robust credit underwriting standards, monitoring loan performance, and proactively managing problem loans. Regularly assessing the creditworthiness of borrowers and the value of collateral is essential.
- Continuous Improvement and Adaptation: The financial landscape is constantly evolving. Successful specialty finance companies must continuously monitor market trends, adapt to changing regulations, and refine their business strategies to stay competitive. This includes leveraging technological advancements and improving operational efficiencies.
Essential Skills and Resources Required for Success
A specialty finance company requires a specific set of skills and resources to thrive. These elements are crucial for navigating the complexities of the industry and achieving sustainable growth.
- Financial Expertise: A deep understanding of financial principles, including credit analysis, risk management, and financial modeling, is essential. Expertise in financial statement analysis, loan structuring, and valuation is crucial for making sound lending decisions.
- Credit Analysis Skills: The ability to assess the creditworthiness of borrowers is paramount. This involves analyzing financial statements, credit reports, and other relevant information to determine the risk of default. Experience with different types of collateral, such as equipment, real estate, and accounts receivable, is beneficial.
- Risk Management Capabilities: Implementing effective risk management strategies is critical for mitigating potential losses. This includes developing and implementing credit policies, monitoring loan performance, and managing problem loans. Experience with risk-based pricing and portfolio diversification is also valuable.
- Legal and Regulatory Knowledge: A thorough understanding of the legal and regulatory landscape is essential. This includes knowledge of lending laws, consumer protection regulations, and industry-specific regulations. Working with experienced legal counsel is crucial for ensuring compliance.
- Technology Infrastructure: Investing in robust technology infrastructure is critical for efficiency and scalability. This includes loan origination software, CRM systems, and data analytics tools. Leveraging technology to automate processes, improve data analysis, and enhance customer service is essential.
- Access to Capital: Securing access to capital is essential for funding loan originations and supporting growth. This may involve establishing relationships with investors, securing lines of credit from banks, or exploring other funding options.
- Strong Network and Relationships: Building a strong network of clients, partners, and industry professionals is essential for generating business and staying informed about market trends. This includes developing relationships with borrowers, referral sources, and other financial institutions.
Importance of Building Strong Relationships with Clients and Partners
Cultivating robust relationships with clients and partners is a cornerstone of success in the specialty finance industry. These relationships foster trust, loyalty, and mutual growth.
- Client Relationship Management: Building strong relationships with clients goes beyond simply providing financial products. It involves understanding their needs, providing excellent customer service, and being a trusted advisor. This fosters loyalty and repeat business.
- Partner Collaboration: Partnering with other businesses, such as equipment vendors, manufacturers, and other financial institutions, can provide access to new clients, increase deal flow, and reduce risk. Establishing strategic alliances can create synergistic opportunities.
- Transparency and Communication: Open and transparent communication with both clients and partners is essential for building trust. This includes providing clear and concise information about loan terms, fees, and risks. Proactive communication helps to manage expectations and resolve issues quickly.
- Responsiveness and Reliability: Being responsive to client and partner inquiries and providing reliable service are crucial for building a strong reputation. Meeting deadlines, honoring commitments, and providing timely support demonstrate professionalism and build trust.
- Ethical Conduct: Maintaining the highest ethical standards is essential for building long-term relationships. This includes acting with integrity, being fair and honest, and adhering to all applicable laws and regulations. Ethical behavior fosters trust and strengthens relationships.
- Long-Term Perspective: Building strong relationships is a long-term investment. Focusing on creating value for clients and partners, rather than solely on short-term profits, is essential for sustainable growth. This approach builds loyalty and creates a foundation for future opportunities.
Marketing and Sales Strategies: Specialty Finance Company
Specialty finance companies thrive on targeted marketing and robust sales strategies. Effectively reaching the right clients and demonstrating value are critical for growth. A well-defined approach, encompassing both online and offline channels, is essential for attracting and retaining customers in this competitive sector.
Developing Effective Marketing Strategies
Developing effective marketing strategies requires a deep understanding of the target market and a multi-faceted approach. This includes identifying the specific needs of potential clients, choosing the right marketing channels, and crafting compelling messaging.
- Market Research and Segmentation: Thorough market research is the foundation. Identify specific niches within the specialty finance landscape and segment the market based on industry, size, and financial needs. For example, a company specializing in equipment financing might focus on construction, manufacturing, or agricultural businesses. Understanding their unique challenges and opportunities is crucial.
- Value Proposition Development: Clearly articulate the unique value proposition. What differentiates the specialty finance company from traditional banks or other lenders? This could be faster approval times, more flexible terms, industry-specific expertise, or a focus on underserved markets.
- Branding and Messaging: Develop a strong brand identity that reflects the company’s values and expertise. The messaging should be consistent across all marketing channels, emphasizing the benefits of working with a specialty finance provider.
- Channel Selection: Choose the most effective marketing channels to reach the target audience. This might include a combination of online and offline strategies.
Methods for Reaching Target Clients
Reaching target clients involves a strategic deployment of various marketing channels. The choice of channels depends on the specific target market and their preferred methods of information consumption.
- Digital Marketing:
- Search Engine Optimization (): Optimize the company website and content to rank higher in search engine results for relevant s. This includes on-page optimization, off-page optimization (e.g., building backlinks), and technical .
- Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising: Utilize platforms like Google Ads and Bing Ads to target specific s and demographics. PPC allows for immediate visibility and targeted advertising.
- Social Media Marketing: Establish a presence on relevant social media platforms (e.g., LinkedIn, Facebook) to build brand awareness, engage with potential clients, and share valuable content. LinkedIn is particularly useful for B2B specialty finance.
- Content Marketing: Create valuable content, such as blog posts, articles, white papers, and webinars, that addresses the needs and interests of the target audience. This helps establish the company as a thought leader and attract potential clients.
- Email Marketing: Build an email list and send targeted email campaigns to nurture leads, promote services, and share industry insights.
- Offline Marketing:
- Industry Events and Conferences: Sponsor or exhibit at industry-specific events to network with potential clients and partners. This provides face-to-face interaction and opportunity to showcase services.
- Direct Mail: Utilize direct mail campaigns to reach specific businesses or individuals with targeted offers and information.
- Print Advertising: Advertise in industry-specific publications or trade journals.
- Partnerships and Referrals:
- Strategic Partnerships: Partner with complementary businesses, such as equipment vendors, accounting firms, or industry associations, to generate referrals.
- Referral Programs: Implement referral programs to incentivize existing clients to refer new business.
Successful Sales Techniques in the Specialty Finance Sector
Successful sales techniques in specialty finance go beyond simply selling a product; they involve building relationships and providing tailored solutions.
- Needs-Based Selling: Focus on understanding the client’s specific financial needs and challenges. Tailor the financing solution to address those needs, rather than pushing a generic product.
- Relationship Building: Build strong relationships with clients based on trust and transparency. This involves consistent communication, responsiveness, and a commitment to providing excellent customer service.
- Consultative Approach: Position the sales team as trusted advisors who can provide financial expertise and guidance. Offer insights into industry trends and help clients make informed decisions.
- Clear and Concise Communication: Explain the terms and conditions of the financing agreement in a clear and easy-to-understand manner. Avoid jargon and be transparent about all fees and charges.
- Negotiation and Flexibility: Be prepared to negotiate terms and offer flexible solutions to meet the client’s needs.
- Follow-Up and Ongoing Support: Provide ongoing support and follow-up after the financing agreement is in place. This helps build long-term relationships and generate repeat business.
Example: A specialty finance company focused on providing working capital loans to e-commerce businesses might leverage to rank for s like “e-commerce financing” and “working capital for online businesses.” They could also create blog content on topics like “How to manage cash flow for your e-commerce business” and “Funding options for growing your online store.” Their sales team could then use a consultative approach, assessing the specific needs of each e-commerce business and offering tailored loan terms based on their sales volume, transaction history, and growth plans. This approach, combining effective marketing with a customer-centric sales process, increases the chances of success in a competitive market.
Specialty finance companies offer niche financial solutions, and understanding their performance is crucial. When evaluating these firms, it’s wise to check resources, and in that vein, exploring reviews on beyond finance can offer valuable insights into customer experiences. Ultimately, assessing feedback helps in gauging the reliability of any specialty finance company you might consider.
Operational Efficiency and Best Practices
Specialty finance companies, operating in niche markets, rely heavily on operational efficiency to maintain profitability and competitiveness. Streamlined processes, robust risk management, and unwavering compliance are crucial for navigating the complexities of their specific financial products and services. Implementing best practices in these areas not only reduces operational costs but also enhances the overall customer experience and fosters sustainable growth.
Key Operational Processes of a Specialty Finance Company
Specialty finance companies have several core operational processes. Each process must be carefully managed for optimal performance.
- Origination: This is the initial phase where potential borrowers are assessed, and loan applications are processed. It involves credit analysis, due diligence, and structuring the financial product. A well-defined origination process ensures that only qualified borrowers are approved, minimizing the risk of default.
- Underwriting: This critical step involves evaluating the creditworthiness of the borrower and the collateral (if any). It determines the terms and conditions of the loan, including interest rates, repayment schedules, and any associated fees. Accurate underwriting is essential for managing credit risk.
- Loan Servicing: This involves managing the loan portfolio after origination. It includes collecting payments, handling customer inquiries, managing delinquencies, and foreclosures (if necessary). Efficient loan servicing is crucial for maintaining a healthy portfolio and ensuring customer satisfaction.
- Funding: This process involves disbursing the approved funds to the borrower. It requires precise execution to ensure that funds are released promptly and accurately, according to the loan agreement.
- Reporting and Analytics: Regular reporting and analysis of key performance indicators (KPIs) are essential for monitoring the performance of the portfolio and identifying areas for improvement. This includes tracking loan performance, delinquency rates, and profitability.
Best Practices for Managing Risk and Ensuring Compliance
Risk management and compliance are paramount for specialty finance companies, especially considering the regulatory environment. These practices help mitigate potential losses and avoid legal issues.
- Credit Risk Management: Implementing robust credit scoring models and conducting thorough due diligence on borrowers are crucial. Regularly reviewing and updating credit policies based on portfolio performance and market conditions is also important.
- Operational Risk Management: This involves identifying and mitigating risks related to internal processes, people, and systems. Implementing strong internal controls, segregating duties, and regularly auditing processes can help minimize operational risks.
- Market Risk Management: Specialty finance companies should understand and manage the risks associated with market fluctuations, such as interest rate changes or economic downturns. Using hedging strategies and diversifying the loan portfolio can help mitigate these risks.
- Compliance with Regulations: Staying up-to-date with all applicable federal, state, and local regulations is essential. This includes adhering to consumer protection laws, anti-money laundering (AML) regulations, and data privacy rules. Establishing a strong compliance program, including regular training and independent audits, is vital.
- Data Security: Protecting sensitive customer data is crucial. Implementing robust data security measures, including encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, is necessary to prevent data breaches and protect customer information.
Procedures for Improving Operational Efficiency within a Specialty Finance Company
Improving operational efficiency requires a multi-faceted approach. These procedures can help streamline processes and reduce costs.
- Process Automation: Automating repetitive tasks, such as loan application processing, payment reminders, and reporting, can significantly improve efficiency. Implementing automated workflows can reduce manual errors and free up employees to focus on higher-value activities.
- Technology Adoption: Leveraging technology solutions, such as customer relationship management (CRM) systems, loan origination systems (LOS), and data analytics platforms, can streamline operations and improve decision-making.
- Process Standardization: Standardizing processes across the organization can reduce variability and improve consistency. This includes creating standardized templates, checklists, and procedures for all key activities.
- Employee Training and Development: Providing ongoing training and development to employees can improve their skills and knowledge, leading to greater efficiency and productivity. This includes training on new technologies, regulatory updates, and best practices.
- Performance Monitoring and Measurement: Establishing KPIs and regularly monitoring performance can help identify areas for improvement. This includes tracking loan origination times, delinquency rates, and customer satisfaction.
- Outsourcing: Outsourcing non-core functions, such as loan servicing or IT support, can allow the company to focus on its core competencies and reduce costs.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly reviewing and refining processes can lead to ongoing improvements in efficiency. This includes soliciting feedback from employees and customers, conducting regular audits, and implementing changes based on performance data.
Industry Associations and Resources
Specialty finance companies operate in a dynamic and complex environment. Staying informed about industry trends, best practices, and regulatory changes is crucial for success. Industry associations and resources provide valuable support and guidance in navigating this landscape. These resources offer networking opportunities, educational programs, and access to critical information that can help specialty finance companies thrive.
Prominent Industry Associations
Joining industry associations provides a wealth of benefits for specialty finance companies. These organizations often serve as the voice of the industry, advocating for favorable policies and providing resources to help members succeed.
- The Commercial Finance Association (CFA): The CFA is a leading global trade association for the asset-based lending and factoring industries. It offers educational programs, networking events, and advocacy efforts. The CFA publishes industry research and provides access to legal and regulatory resources.
- The American Financial Services Association (AFSA): AFSA represents the consumer credit industry, including finance companies, auto finance companies, and mortgage lenders. They provide advocacy, education, and networking opportunities for their members. AFSA monitors legislative and regulatory developments affecting the industry.
- The Equipment Leasing and Finance Association (ELFA): ELFA is the premier trade association for companies in the equipment finance sector. It offers resources for businesses involved in equipment leasing and financing, including industry data, education, and advocacy.
- The National Association of Government Guaranteed Lenders (NAGGL): NAGGL focuses on the Small Business Administration (SBA) lending market. They provide training, resources, and advocacy for lenders participating in SBA programs.
- Regional and State-Specific Associations: Numerous regional and state-level associations cater to the specific needs of specialty finance companies within a particular geographic area. These organizations often offer targeted networking opportunities and regulatory updates.
Benefits of Joining Industry Associations
Membership in industry associations offers several advantages for specialty finance companies. These benefits contribute to improved performance and long-term sustainability.
- Networking Opportunities: Associations provide platforms for connecting with peers, potential partners, and industry experts. These connections can lead to new business opportunities and collaborations.
- Educational Resources: Associations offer training programs, webinars, and conferences that provide insights into industry trends, best practices, and regulatory changes. This helps members stay informed and improve their skills.
- Advocacy and Government Relations: Associations actively lobby on behalf of their members, advocating for policies that support the specialty finance industry. They monitor legislative and regulatory developments and work to shape favorable outcomes.
- Access to Industry Data and Research: Many associations publish industry reports, surveys, and data that provide valuable insights into market trends, performance benchmarks, and competitive landscapes.
- Best Practice Guidelines: Associations often develop and disseminate best practice guidelines to help members operate efficiently and ethically.
Staying Informed About Industry Trends and Best Practices
Staying informed about industry trends and best practices is crucial for the success of specialty finance companies. This involves proactively seeking out information from various sources.
- Industry Publications and Newsletters: Subscribing to industry-specific publications, newsletters, and blogs provides regular updates on market trends, regulatory changes, and best practices.
- Market Research Reports: Purchasing or accessing market research reports from reputable firms provides in-depth analysis of industry trends, competitive landscapes, and growth opportunities.
- Webinars and Online Courses: Participating in webinars and online courses offered by industry associations and other educational providers helps to acquire new skills and stay up-to-date on the latest developments.
- Conferences and Trade Shows: Attending industry conferences and trade shows provides opportunities to network with peers, learn about new products and services, and gain insights into emerging trends.
- Benchmarking Against Peers: Comparing your company’s performance against industry benchmarks and best practices helps identify areas for improvement and drive operational efficiency.
Specialty finance companies, often dealing in niche lending, require a strong online presence to attract clients. A well-designed website is crucial, and understanding the principles of finance website design ensures user trust and engagement. Ultimately, a visually appealing and user-friendly website helps specialty finance companies effectively showcase their services and build credibility in a competitive market.